Read, hot & digitized: Librarians and the digital scholarship they love — In this series, librarians from the Libraries’ Arts, Humanities and Global Studies Engagement Team briefly present, explore and critique existing examples of digital scholarship to encourage and inspire critical reflection of and future creative contributions to the growing fields of digital scholarship.
The Quantitative Criticism Lab (QCL) was formed in 2014 as a collaboration between humanists, computer scientists and computational biologists. The project’s unique combination of expertise informs its innovative approach to the computational analysis of Latin literature. And I’m not just saying that as a research assistant for the project!
The lab is led by Pramit Chaudhuri, an Associate Professor of Classics at the University of Texas at Austin, and Joseph Dexter, a computational biologist and Neukom Fellow at Dartmouth. They recruited me before I knew what digital humanities was, though I was certain that I wanted to do something more with my Classics undergraduate degree other than teaching fifth graders “Heads, Shoulders, Knees and Toes” in Latin (“Caput, umeri, genua and pedes”, if you were wondering).
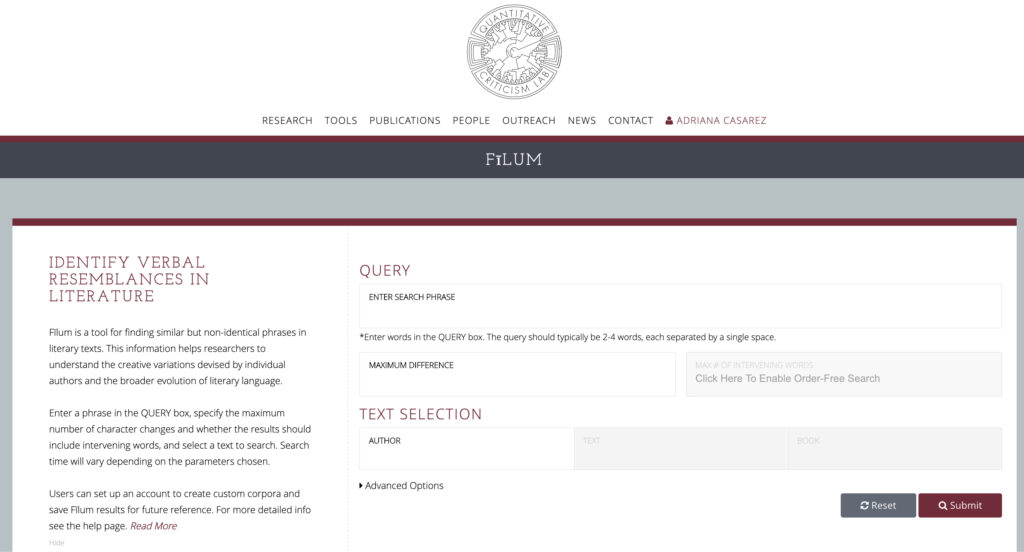
This digital Classics project uses machine learning, natural language processing and systems biology to study Latin literature and its influence. QCL uses a computational approach to explore the traditional study of “philology”, or the development and history of language in text. The lab’s first development was its tool, Fīlum (Latin for the thread of a web), an apt name given the tool’s purpose to reveal relationships amongst Latin texts by identifying intertextual references in Latin literature.
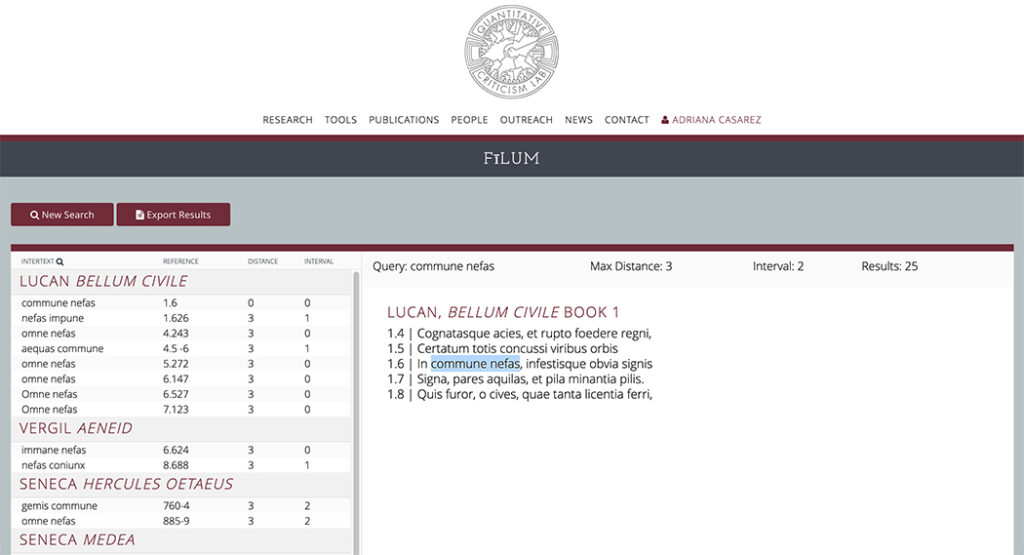
For an example of intertextuality, in the epic poem the Aeneid, Vergil uses the phrase “immane nefas”, meaning “huge wrongdoing” to refer to the unspeakable horrors of the underworld. Years later, the author Lucan, in his epic, the Pharsalia, references and adapts that phrase to “commune nefas”, or “collective wrongdoing”, to blame an entire community for the horrors of civil war. Fīlum aids scholars in discovering, tracking, and discussing such connections.
So, what makes Fīlum better than a ctrl+f approach? In the example above, a scholar would have to search many texts to even possibly discover Lucan’s reference; with Fīlum, they can search many texts simultaneously. Furthermore, Fīlum can even detect phrasing similar to the search query.
QCL’s computational approach tabulates similarity, using the concept of “edit distance”, or the number of character changes through additions, deletions or substitutions in two words or phrases. For example, the edit distance of “kitten” and “sitting” has an edit distance of 3. You substitute “k” with “s”, “e” with “i”, and add a “g” – three changes in total.
What if you have a feeling the phrase you want to use in Fīlum, might be in a different word order? With “Order-Free” searching, the tool searches for any arrangement of the words in a phrase. This is an especially valuable feature since Latin often refuses to follow a regulated pattern of word order.
With its search phrase, edit distance and order free option, Fīlum searches through a selected text or a user-selected corpora of Latin literature from the site. With a free account, users can create a search corpus from a library of texts or upload their own.
The output cleanly displays results distinguished by each text’s author, work, and highlights the relevant words in each result. For added context, when selected, each result displays the previous and following lines from the text for context.
I have enjoyed both working on Fīlum and using the tool for my research. As QCL continues to improve the tool, I hope other classicists will appreciate not only its value but the interdisciplinary method that built it.
If you are interested in the project and its study, please stay tuned to information about an upcoming QCL sponsored conference in April, here on the UT Austin Campus:
Digital Humanities Beyond Modern English: Computational Analysis of Premodern and Non-Western Literature https://qcrit.github.io/DHBME/
For further reading on topics like digital classics and text analysis, please see below:
Text Analysis with R for Students of Literature by Matthew L. Jockers.
Philology : the forgotten origins of the modern humanities / James Turner.
UT Library Libguide on Text Analysis by European Studies Librarian, Ian Goodale