Read, hot & digitized: Librarians and the digital scholarship they love — In this series, librarians from the Libraries’ Arts, Humanities and Global Studies Engagement Team briefly present, explore and critique existing examples of digital scholarship to encourage and inspire critical reflection of and future creative contributions to the growing fields of digital scholarship.
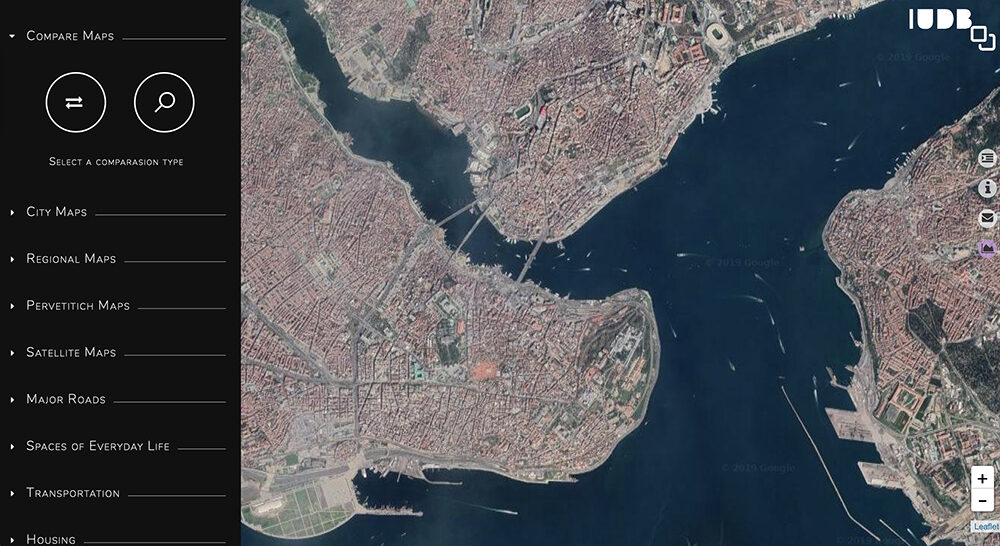
The Istanbul Urban Database project, headed by Nil Tuzcu (MIT), Sibel Bozdoğan (İstanbul Bilgi), and Gül Neşe Doğusan Alexander (Harvard), seeks to preserve collective memory and the urban cultural heritage of Istanbul by becoming the most comprehensive online archive of Istanbul’s urban history. The project is based on a digital corpus of maps of Istanbul, aerial imagery, photographs, and geographical features. The project combines this wide range of historical data on a sustainable platform that can be integrated into other projects. The project does not stand alone; there is, in fact, an API in development for serving and exporting the various layers of the information it contains.
With the Istanbul Urban Database, users can select a variety of maps, photos, and other imagery to superimpose over one another, or compare. You can examine one historical map at a time, superimpose them with adjustable transparency, and overlay georeferenced features on the maps. The side-by-side tool allows users to compare maps from two different time periods (currently limited to the 19th and 20th centuries). Uniquely, the project draws on Ottoman and French maps, primarily from the Harvard Map Collection. This allows the user to get a sense of both the internal and external views of Istanbul in the early 20th century.
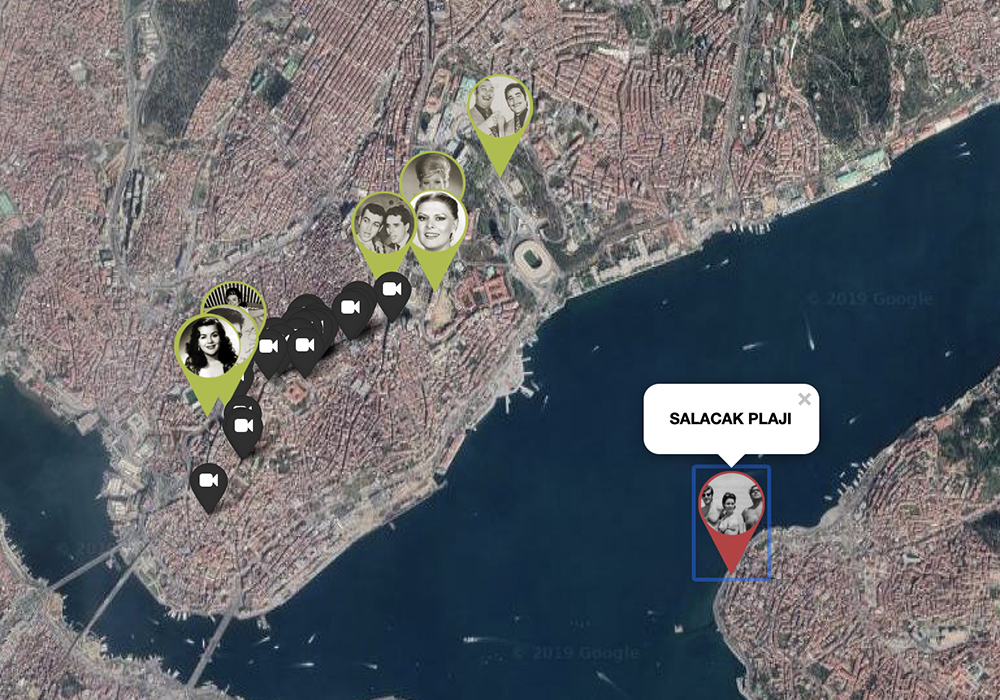
In terms of infrastructure, the Istanbul Urban Database’s transportation layer hosts information drawn from a 1922 map on ferry, train, and tramway lines. The project organizers decided to present major roads separately because of their impact on city growth. The ferry, train, and tramway lines, and the roads, were drawn by Harvard Mellon Urban Initiative researchers––a quite labor intensive process from which users benefit immensely. Users also will enjoy having access to Henri Prost’s master plan archives, which have had significant effect on the development of the city of Istanbul. Lastly, users can peruse photographs of everyday life at different points in Istanbul’s history. Examples include beaches, casinos, movie theaters, and patisseries; snapshots of lives well-lived so long ago, in some cases in places that no longer exist.
The Istanbul Urban Database project is significant for its combination of resources on an accessible platform with potential for applications in other projects. Istanbul is a difficult city to navigate, let alone understand, today, and so attempting to imagine its past lives might seem rather intimidating for researchers. The Istanbul Urban Database project streamlines access to crucial 20th and late-19th century resources to facilitate research on the growth, structure, and development of the city of Istanbul.
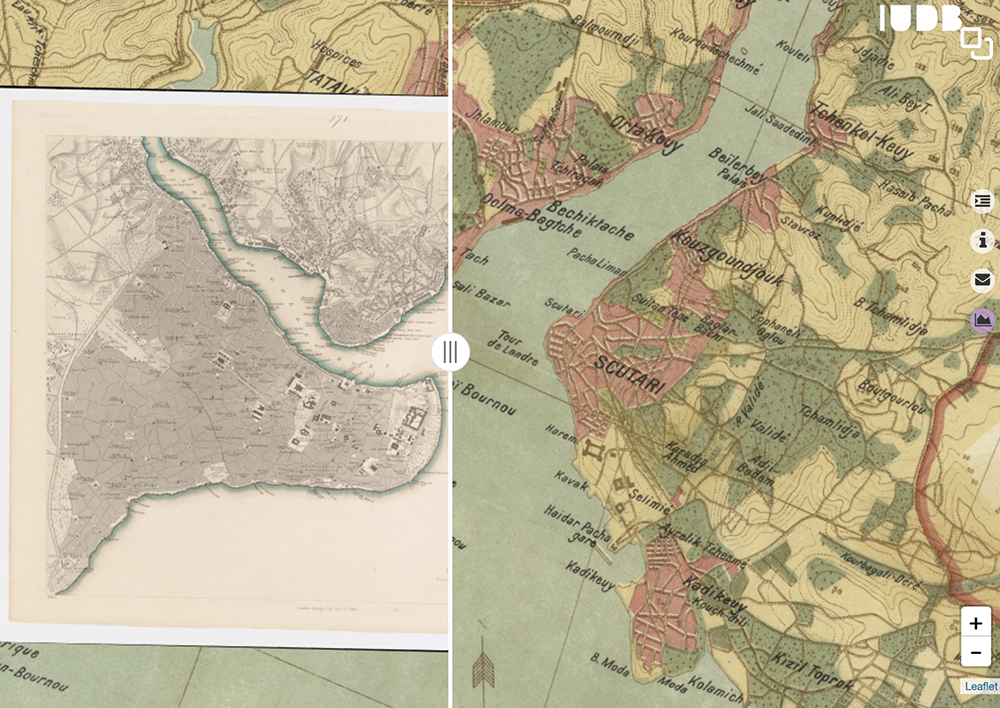
I encourage readers to explore all of the tools available, especially the comparison tool that allows you slide two maps right and left to compare time periods. I also suggest looking through the photographs of everyday life that are exhibited through this project, and examine whether or not these places still exist today by zooming into the base satellite map. Readers who are interested in maps of Istanbul and Turkey more broadly would benefit from visiting the UT Maps Collection. The maps of Turkey and specifically Istanbul are extensive and of interest for those piqued by the Istanbul Urban Database.

