Read, hot & digitized: Librarians and the digital scholarship they love — In this new series, librarians from UTL’s Arts, Humanities and Global Studies Engagement Team briefly present, explore and critique existing examples of digital scholarship. Our hope is that these monthly reviews will inspire critical reflection of and future creative contributions to the growing fields of digital scholarship.
For most of human history, poetry has been an oral tradition, with poets singing their verses to an audience rather than writing them down and disseminating them in print. Italianpoetry.it, an independent digital humanities project without academic affiliation, aims to share the beauty and lyricism of recited Italian poetry with a wider audience, offering recordings of Italian poems alongside the original text and English translations.
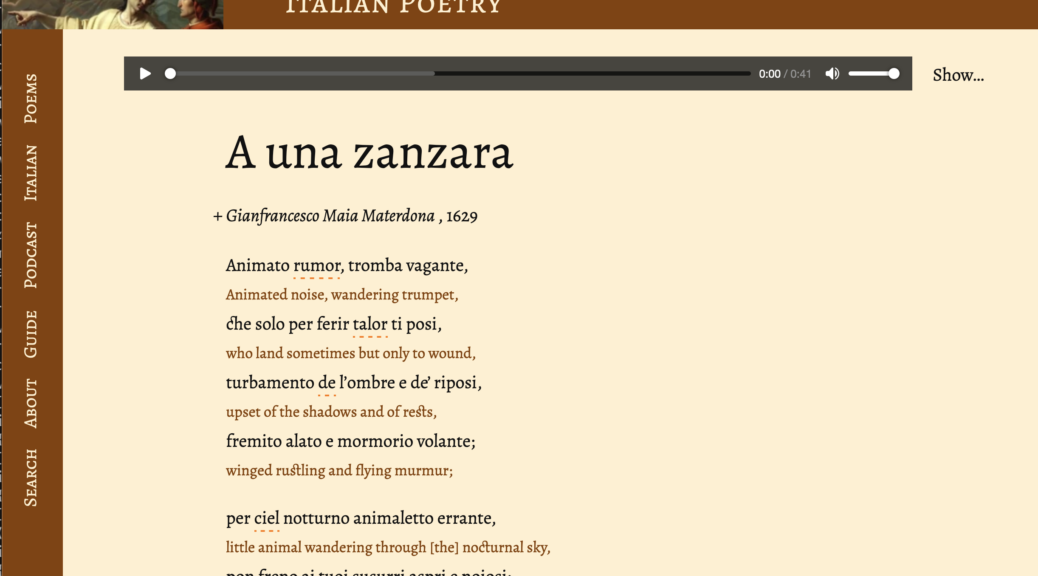
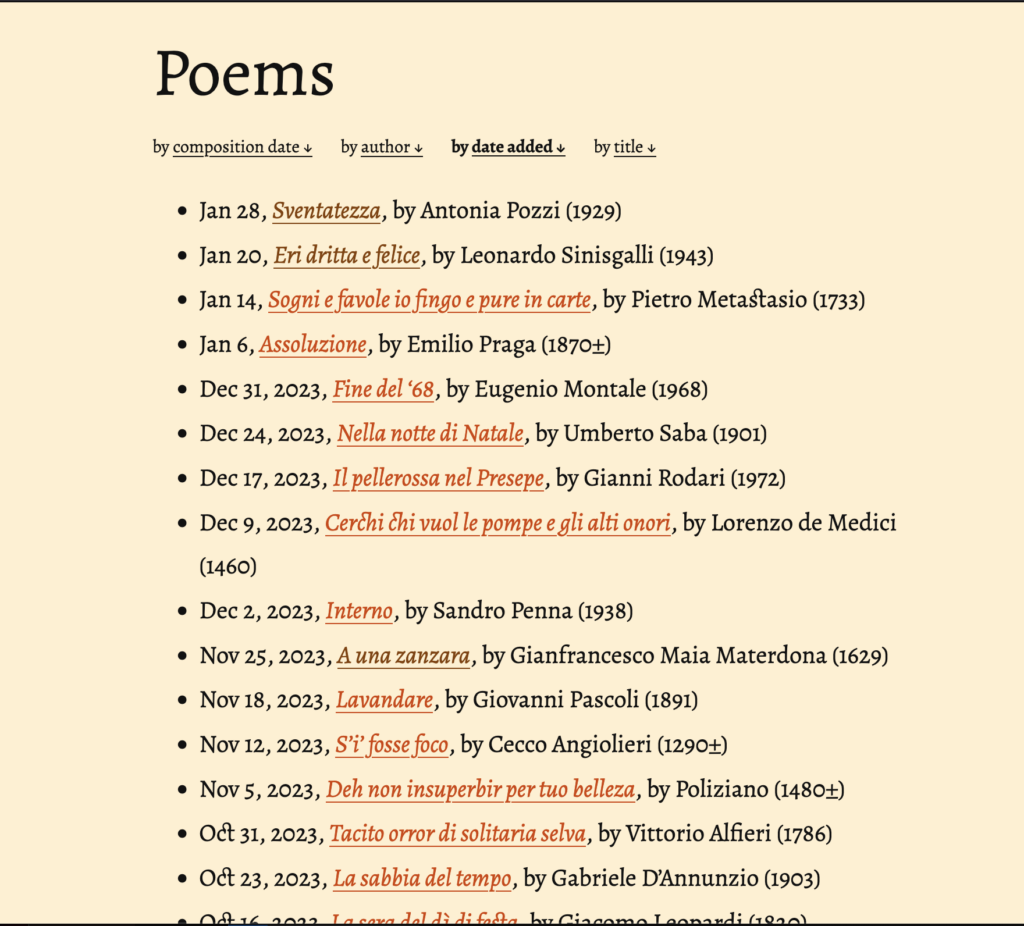
The site, which is frequently updated with new poems, focuses on a simple but very effective content model. Poems are published in their entirety in the original Italian, with the English translation of the text beneath each line. An audio file containing the recording of the poem is embedded at the top of each page. When the audio file is played, the word being read is highlighted in both the Italian and the English translation, allowing users to follow along with the recording and to see how the word order and phrasing in the translation compares to the original text. This allows for a streamlined, user-friendly experience that facilitates appreciation and enjoyment of the original text—both for its sonority and its meaning—regardless of the user’s knowledge of Italian. Each poem also has a brief write-up by the site’s creator at the bottom of the page, providing additional context for the work. A guide to navigating the site is also provided to make it easy for new users to interact with its content.

The site is intentionally simple and, per the author, “unapologetically retro-looking” in its appearance, allowing users to focus on the site content without interference from unnecessary or distracting web elements. Focusing on simplicity is not only an aesthetic choice, though, as it helps make the site more accessible for users with slower or unstable internet connections who may have trouble browsing more complex webpages. The site uses the BAS Web Services set of tools to synchronize the poems’ texts with the audio recordings. The BAS Web Services are provided by the Bavarian Archive for Speech Signals, and provide a broad and valuable set of tools for speech sciences and technology.
In addition to the main pages created for each poem, there is also an audio-only podcast version of the poems for those who would like to listen to the audio without the interactive elements of the main site. The site’s creator makes clear that the poems selected are in no way representative of Italian poetry as a whole, and that they were chosen at the author’s discretion. This adds a personal touch to the site sometimes absent from more comprehensive digital projects.

Italianpoetry.it is a valuable resource for those wishing to explore Italian poetry, regardless of their experience with the Italian language or knowledge of its history. While intentionally a personal selection rather than a wide-ranging survey of the Italian poetic tradition, its content offers a great introduction to that tradition that can spur further interest and exploration. It also provides a very interesting and accessible way to explore the relationships between written and spoken text, sonority and textual structure, and translation and original texts.
For more information, please consult the UTL resources below:
Picchione, John, Lawrence R. Smith, John Picchione, and Lawrence R. Smith. Twentieth-Century Italian Poetry : An Anthology. Toronto: University of Toronto Press, 2019.