Read, hot & digitized: Librarians and the digital scholarship they love — In this series, librarians from UTL’s Arts, Humanities and Global Studies Engagement Team briefly present, explore and critique existing examples of digital scholarship.
This Is Not an Atlas is a continuation of a book of the same name, subtitled “A Global Collection of Counter-Cartographies.” Critical geography proposes that maps are never neutral, but rather reflect views of the map maker, often those in power. Counter-mapping, or creating counter-cartographies, refers to the use of maps to reframe the world in such a way as to challenge dominant power structures and to articulate alternative, progressive and even radical interests (Kitchin, et al., 2011).
In the spring of 2015, kollektiv orangotango, a self-described network of critical geographers, friends, and activists who deal with questions regarding space, power, and resistance, sent out a call for maps in English, German and Spanish. Overwhelmed by the response and realizing that many of the maps submitted are dynamic, they decided to create a website to, not only highlight projects from the print edition, but also to “continue to share maps, struggles, projects, texts, and inspirations online.” Here I highlight a counter-mapping project that successfully deals with the politics of in/visibility, as described in Emancipatory Mapmaking: Lessons from Kibera.
Map Kibera was initiated after a group of geographers attending a mapping conference in Nairobi, Kenya noticed that Kibera, one of Africa’s largest informal settlements, was not mapped. In fact, they discovered that authorities had labeled and designated the Kibera Slum as a forest. How could a community with an estimated population of 250,000 people be omitted from official maps of Nairobi? Two geographers who were also interested in open source mapping decided they wanted to change this. In October 2009, Mikel Maron and Erica Hagen started the Map Kibera project to address “the glaring omission of roughly a quarter-million of Nairobi’s inhabitants from mass communications and city representation and policy decisions” (Hagen, 2011).
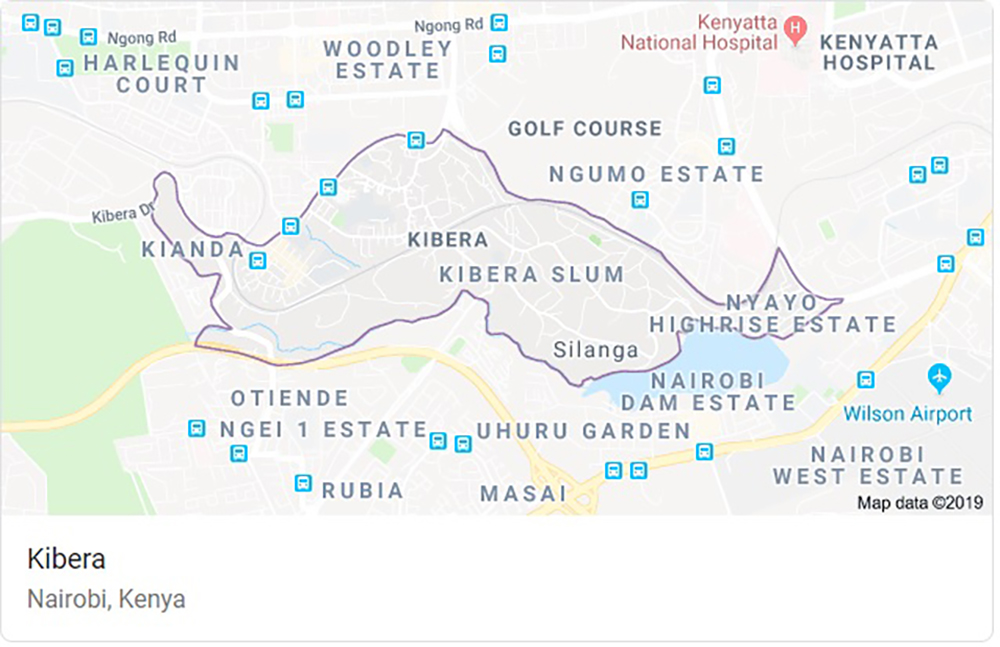
Kibera is too densely populated to rely on satellite data for mapping. Maron and Hagan knew they would need to map it from the ground. They recruited a dozen young residents to be “mappers,” gave them GPS devices, and sent them to collect data by creating “traces,” a GPS-enabled process that tracks and records your physical location. The mappers interviewed residents and collected observational data, such as the names of clinics, schools, and businesses, locations of water pumps, public baths, and other “points of interest” along their routes as well. The team then added the data to OpenStreetMap (OSM), a crowdsourced world map that relies on user-generated content to create geographic data that is relevant and available to everyone. And within three weeks they had created an incredibly dense map of Kibera for the world to see. But more importantly, a map of Kibera that was extremely useful to residents.
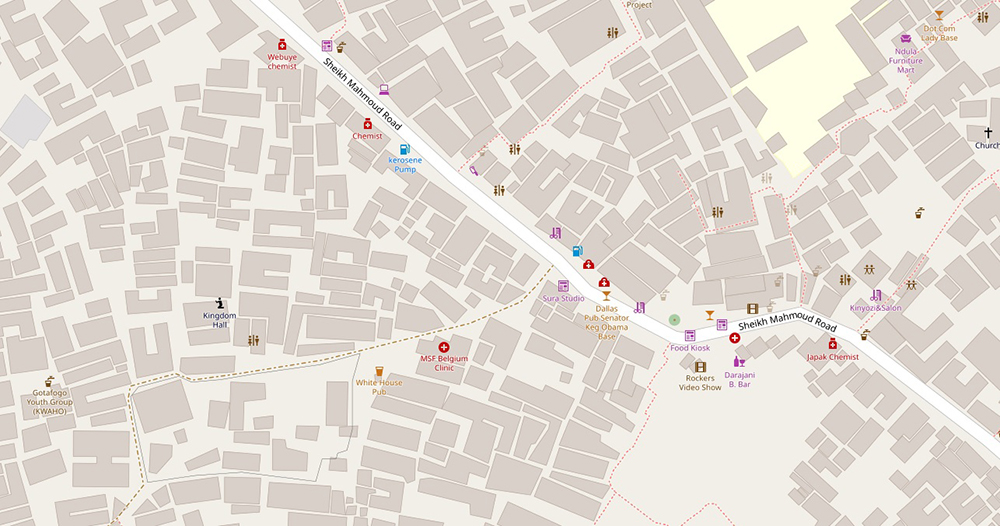
The project did not stop there; they immediately created, printed, and distributed maps of clinics and schools within the community. And a security map of Kibera warning of areas to avoid and illustrating places to get help. And have since formed the Map Kibera Trust, created the Voice of Kibera, a platform for citizen reporting, and replicated their model in other marginalized communities in Nairobi.
Map Kibera is just one counter-mapping project highlighted in This Is Not an Atlas. Visit the site to discover situational maps defending traditional territories of the Amazon; a documentation of human rights violations in Rio de Janeiro’s Favelas; an anti-eviction mapping project that started in the Bay Area and has expanded its scope; a crowdsourcing project that helps people locate public toilets in an Indian megacity; and many more counter-cartographies.
The book is as beautiful as the website; visit the UT Libraries to see it in person. If you’re interested in learning more about critical geography and counter-mapping, I highly recommend Rethinking the Power of Maps and the Map Reader. Map Kibera initiators, Erica Hagen, and Mikel Maron later founded the Ground Truth Initiative. Visit their project page to find out about other counter-mapping projects they are working with, such as Grassroots Jerusalem.

