Anusha Ravi, a Scholars Lab Graduate Research Assistant (GRA), is entering her second year in the School of Information Science, specializing in Data Science and Analytics. During the last academic year, she undertook a Digital Scholarship Project as part of her GRA position. Collaborating with the Collection Development team, she cleaned, analyzed, and visualized data they had collected over the past few years.
I am a passionate data analyst with a keen interest in leveraging data to drive meaningful insights and decisions. My recent work at Scholars Lab Graduate Research Assistant(GRA) has given me a valuable opportunity to apply my skills in a real-world setting, addressing practical challenges and contributing to the enhancement of our informational resources present at the library. My journey in data science is driven by a curiosity to explore data intricacies and a commitment to using technology for the greater good. As part of my responsibilities, I have to complete a digital scholarship project.
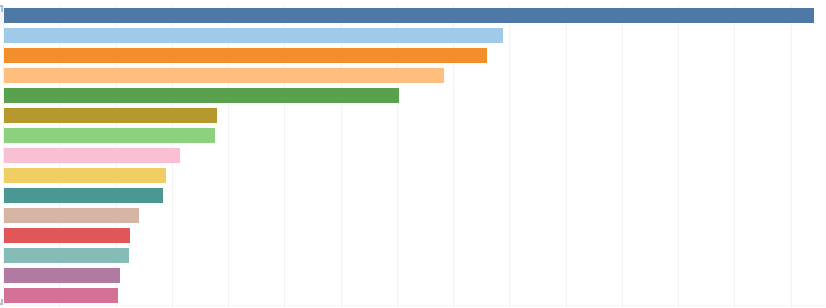
As my digital scholarship project, I worked with the Collection Development team on improving the process of handling suggested purchase requests. These requests are crucial as their analysis would help them understand and enhance the breadth and depth of the collections available in the library. My role involved exploring historical data to identify gaps and understand its structure thoroughly for future enhancements. Collaborating with the Collection Development team who are my stakeholders, I ensured their needs were clearly understood and actionable. This collaborative approach not only enriched my perspective but also aligned our efforts with the library’s strategic goals.
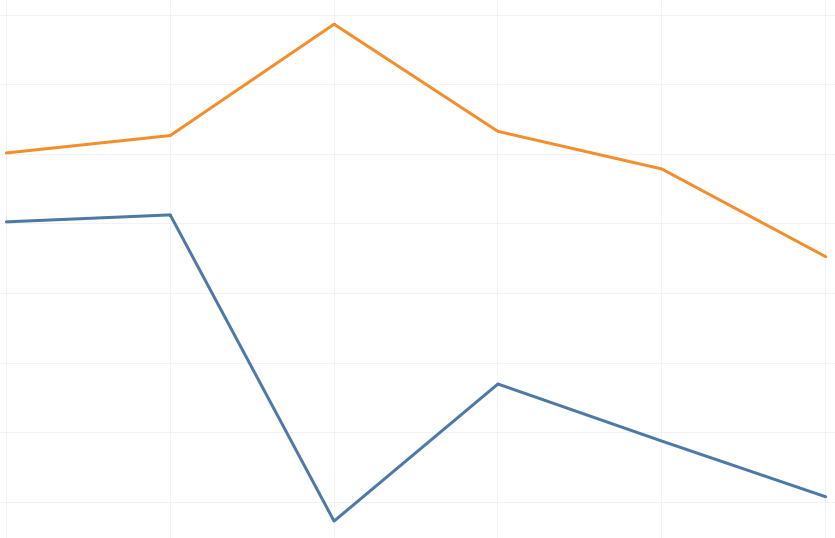
Using Python, I undertook the task of cleaning and anonymizing the data. Fixing missing values and ensuring data confidentiality was challenging, yet automating these processes was a significant achievement. Python’s versatility and powerful libraries were instrumental in this endeavor. Looking ahead, I aim to deepen my expertise in Python to automate more complex data workflows and improve efficiency further. Learning to automate this process was a big challenge, but overcoming it was a significant achievement. I had to code with a future use case in mind, which proved to be very insightful and thereby allowed me to improve my skills.
For data visualization, I turned to Tableau, known for its user-friendly interface and powerful visualization capabilities. Creating interactive and simple charts made it easier to communicate complex data insights to non-technical stakeholders. This was confirmed on presenting this dashboard to the Collection Development team who praised the simple but effective dashboard. Additionally, based on their feedback, I plan to create documentation on using Tableau to ensure easy navigation for future use of the team.
The Scholars Lab provided invaluable support, offering resources and expert advice that enhanced my analysis. Presenting my findings at a poster session was a highlight, showcasing the success and the practical recommendations for better data organization and future collection improvements. This project taught me the importance of stakeholder collaboration, secure data practices, and the continuous quest for automation and efficiency in data processes.