As we’ve spent the last several months gathering information and feedback from the campus community regarding the future of the University of Texas Libraries, more than once we’ve encountered the response, “I wasn’t aware the Libraries did that.”
Too often, the support that libraries provide to users goes unnoticed. Much like electricity or running water, the services and resources that backstop the central work of research and learning at the university don’t get much attention unless something prevents them from being available. Students routinely assume that the Libraries’ website just leads them to other websites that have the articles they need. Researchers who access journals directly from web searches in their offices can’t understand why going to those same links when they’re off campus generates a page requesting payment for a resource. Users rarely conceive how a book requested through interlibrary service can arrive in their hands from points across the globe in a few short days.
Libraries tend not to focus much attention on blowing their respective horns. Mostly they’re too busy bootstrapping the work they’re expected to do. But they’re also doing the unexpected, especially in areas of need associated with reliance on modern technology. So let’s take a look at how the Libraries Information Technology (LIT) team spends their time when they’re not keeping a website that serves 10 million people a year running or managing the hundreds of computers and providing support for the untold volume of hardware and software required by a top-tier academic library.
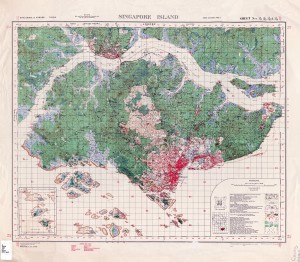
The Libraries has discernible connections to complementary organizations on campus like the Harry Ransom Center and the Briscoe Center for American History; the historical ties to these collections are long-standing, and the Libraries is an ever-present supplementary resource for researchers at those campus gems. But our LIT team also provides the technical backend support for the HRC and Briscoe Center that allows them to focus efforts and resources on more essential work. They administer the Ransom Center’s staff portal that provides support for the professionals that care for the center’s world-class collections. And our team have helped to build and manage several sites that provide web access to the Briscoe Center’s high profile collections, including the archives of journalist Dan Rather and former Texas Governor Bill Clements and provide the digital versions of the center’s Sanborn Fire Maps collection.
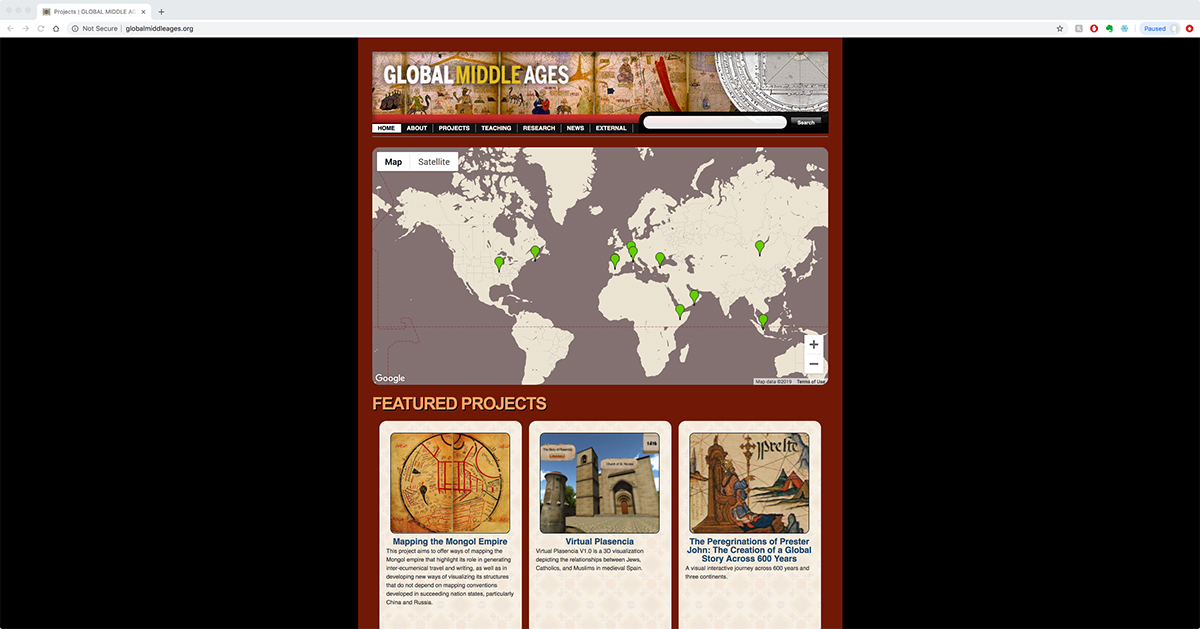
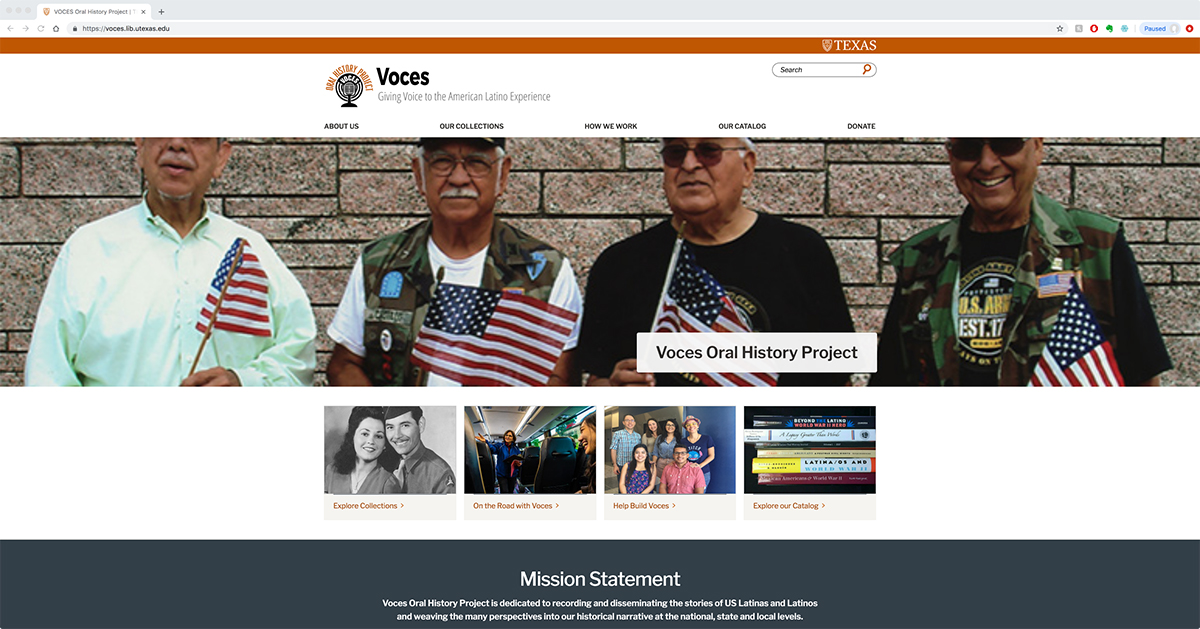
LIT also plays a central role in developing digital scholarship tools with researchers and faculty from across campus, but especially heavily in the area of digital humanities. For more than 10 years, the Libraries has worked in the creation and management of Voces, a Latino/a experience oral history site developed by Dr. Maggie Rivas-Rodriguez of the Moody School of Communications; Voces celebrated a relaunch of their enhanced website last year. The Libraries worked with associate professor of English and comparative literature Geraldine Heng to build a web portal for to the digital resources collected through the Global Middle Ages Project for collaboration among scholars to weave together independent work into a cohesive resource. LIT has also worked with Liberal Arts Instructional Technology Services (LAITS) to support the digital efforts of the Archive of the Indigenous Languages of Latin America (AILLA), which will include resultant work from an NEH grant AILLA received last year.
Libraries’ technology expertise is also deployed in service of academic units around campus in support of learning and research on campus, by helping to provide access to departmental-specific digital collections. Faculty in the College of Fine Arts (COFA) relies heavily upon the Fine Arts Library’s digital image collections for teaching, and staff in the library coordinate with LIT to make those resources available through the portal to the Visual Resources Collection.

The support our LIT staff provides extends far afield of campus, too. Significant global partnerships — especially those connected to efforts at the Benson Latin American Collections — have been reliant on core contributions from the Libraries. Initial work developing a landing site (Kigali Memorial Centre) for the Kigali Genocide Memorial, where digital records of the survivor testimonies reside, were handled by Libraries’ IT staff in coordination with Benson archivists and KMC staff. The Libraries’ also provided the resources for the construction of Primeros Libros, an international effort by collecting institutions to digitize the first books published in the Americas. One of the most notable and controversial projects endeavored by the Libraries was to help facilitate the digital preservation of the Guatemalan Police Archive (AHPN), a cache of over 10 million documents that provides evidence of human rights violations in the Central American country between 1960-1996; LIT has helped to build, maintain and enhance the web resources of this project since its inception, ensuring that this important record won’t be lost to sociopolitical transitions in the region. More recently, staff from LLILAS Benson Latin American Studies and Collections and the LIT team have been building upon a project — initially funded from a 2014 Mellon grant award — that takes a more comprehensive approach to preserving the culture and history of Latin America. The Latin American Digital Initiatives (LADI) repository represents multiple collections shared through the practice of post-custodial archiving to catalog digital resources provided by our southern neighbors.

Beyond their hands-on expertise, Libraries’ technology professionals have accepted roles on various committees across campus to help guide university policies in technology and digitization, currently holding seats on the Central IT Executive Commission and Identity & Access Management Committee. Our staff are not just regarded for their excellence in libraries, they are recognized as leaders in the field.
The stereotype still prevails at times, but it’s worth reinforcing: the library is not simply a book storehouse. It is an active participant in the digital environment, and essential – though much of the time, behind the curtain – to the successful work of others.
Though the lights will on occasion go off, and the water may cease to flow, our committed experts doing their best to make sure that on normal days, things are working better than they should and library users are none the wiser.