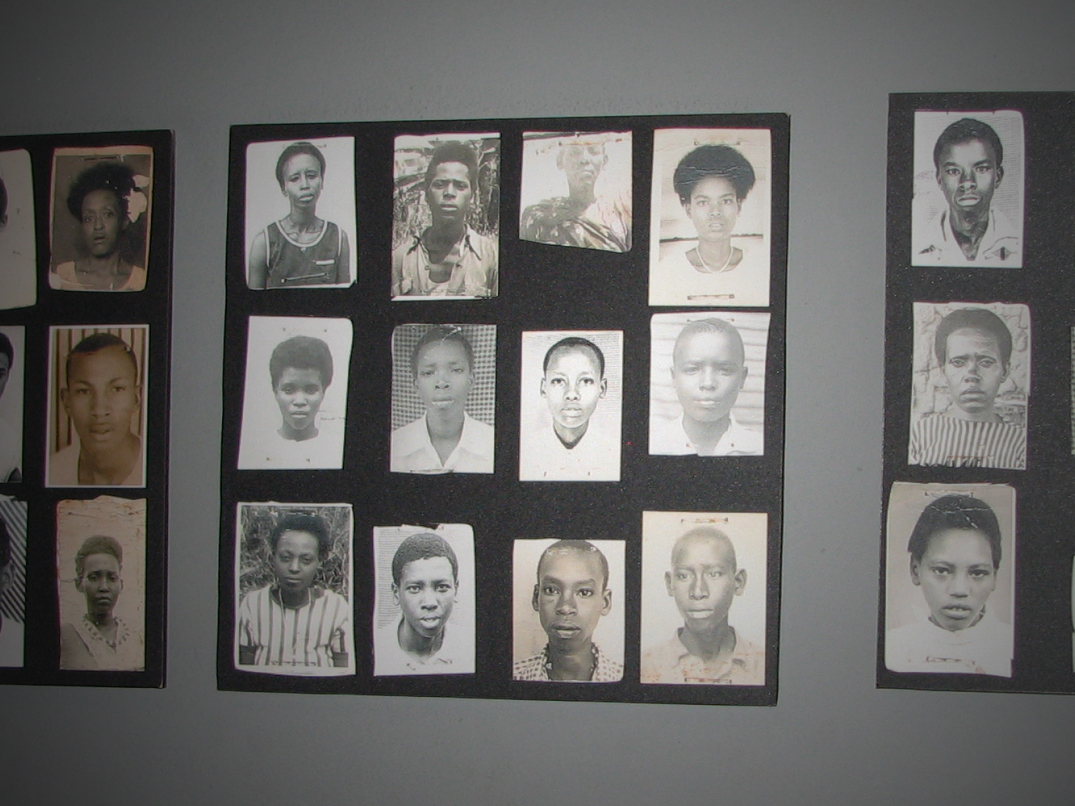
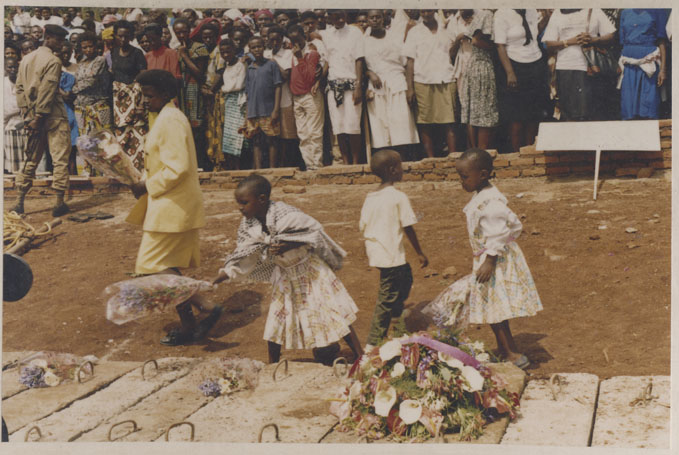
By DAVID A. BLISS
The Human Rights Documentation Initiative (HRDI) is a collaborative archival project aimed at preserving and promoting the use of fragile human rights records from around the world, in order to support human rights advocates working for the defense of vulnerable communities and individuals. The HRDI was established at the University of Texas Libraries with a generous grant from the Bridgeway Foundation in 2008. Additionally, the Human Rights Documentation Initiative has partnered with the Bernard and Audre Rapoport Center for Human Rights and Justice to identify key strategic issues for the initiative as well as provide relevant programming to the UT Austin community and beyond.
The HRDI preserves and provides access to paper-based collections, as well as digitized and born-digital audiovisual collections that are global in scope. Recognizing the importance of online human rights advocacy and the fragility of web content, the HRDI also maintains an archive of websites related to human rights issues, which is updated quarterly.
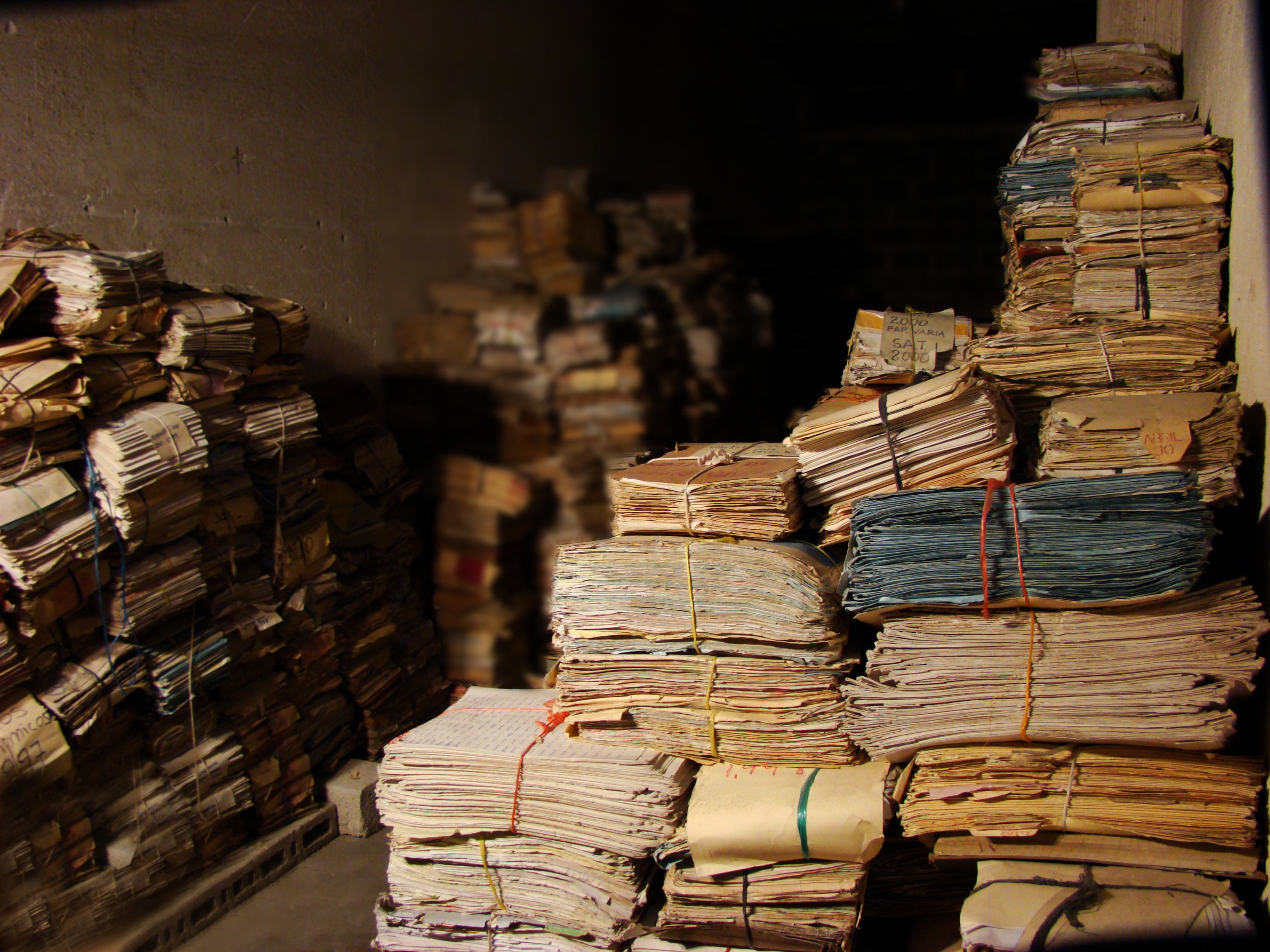
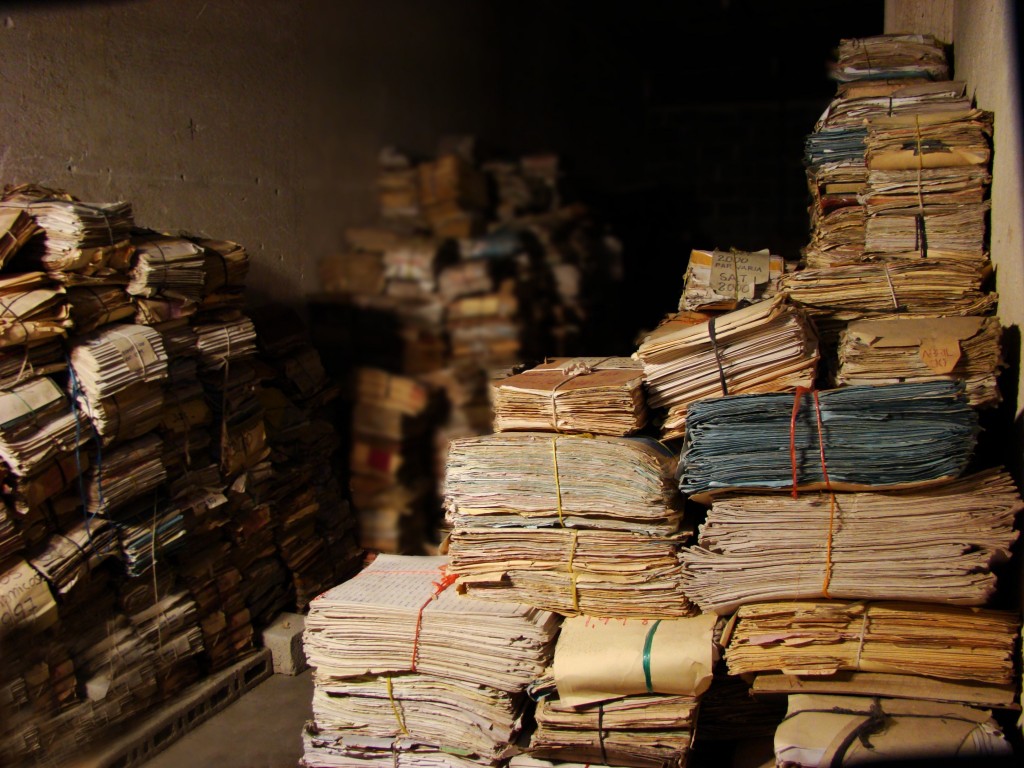
A number of the collections found on this site have been preserved and made available through post-custodial archival collaborations between the HRDI and partner organizations and repositories. Post-custodialism is a collaborative approach to providing access to archival collections that preserves physical archives within their original contexts of creation while also creating digital copies for wider access. Through these collaborations, the HRDI aims to support the development of partners’ archival capacity, particularly in the areas of digitization, preservation, arrangement, description, and access.
About the New Platform
The new version of the HRDI site integrates streaming, search, and browse functionality alongside information about each project partner and the HRDI web archive in a single mobile-friendly interface. To fully accommodate international audiences, several pages are available in both English and Spanish, including those describing Spanish-language collections. The previous HRDI website launched in 2008 and was retired in 2020, when Adobe Flash was discontinued. An archived copy of the previous site and the retired HRDI blog are each available via the Wayback Machine.
Selections
Radio Venceremos, the rebel radio station that broadcast from the mountains of Morazán, El Salvador, during the eleven-year Salvadoran Civil War (1981–1992), produced an important collection of recordings that contain valuable historic, anthropological, and ethnographic information, particularly in regards to human rights violations during an era of social transformation in Central America. This recording from December 31, 1981, contains an interview with Rufina Amaya about the massacre at El Mozote: Radio Venceremos Recording
Chammah and Young 1976 Oral History on the Jewish Community in Syria
Four-part account of Albert Chammah and Oran Young’s 1976 visit to Syria to investigate the political, social, and economic status of the Jewish community there. The account details the contemporary size of the Jewish communities in several Syrian cities, formal restrictions imposed by the Syrian government, and general social discrimination. Albert Chammah was a professor at UT Austin, while Oran Young was a graduate student at the time: Conversation between Albert Chammah and Oren Young
This account was transferred from two cassette tapes, donated to the HRDI by Albert Chammah’s son Maurice. Maurice Chammah is an Austin-based journalist and staff writer for The Marshall Project, focusing on capital punishment and the criminal justice system in the United States.
TAVP: Texas After Violence Project
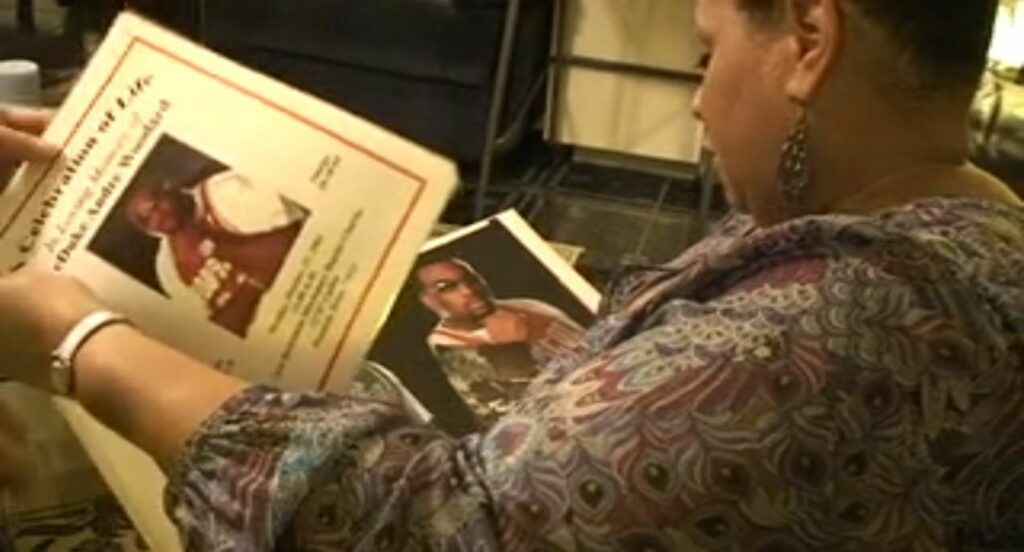

Texas After Violence Project (TAVP) is a human rights and restorative justice project that studies the effects of interpersonal and state violence on individuals, families, and communities. The collection includes hundreds of hours of personal testimony that serves as a resource for community dialogue and public policy to promote alternative, nonviolent ways to prevent and respond to violence. Watch: Interview with Donna Hogan
David A. Bliss is digital archivist at the University of Texas Libraries.






















