By DANIEL ARBINO
Vea abajo para versión en español
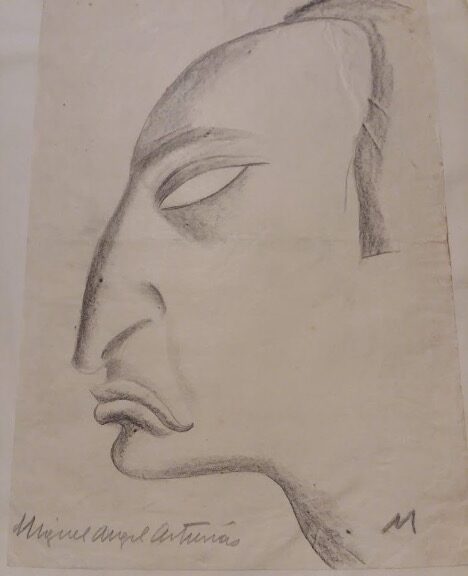
The Nettie Lee Benson Latin American Collection is thrilled to announce the acquisition of the Miguel Ángel Asturias Papers. Asturias, the 1967 Nobel Laureate in Literature from Guatemala, was a precursor to the Latin American Boom. A prolific writer of poetry, short stories, children’s literature, plays, and essays, he is perhaps best known as a novelist, with El Señor Presidente (1946) and Hombres de maíz (1949) garnering the most acclaim. Asturias’s portrayal of Guatemala and the different peoples that live there—their beliefs, their interactions, their frustrations, and their hopes—mark the profundity of his texts.
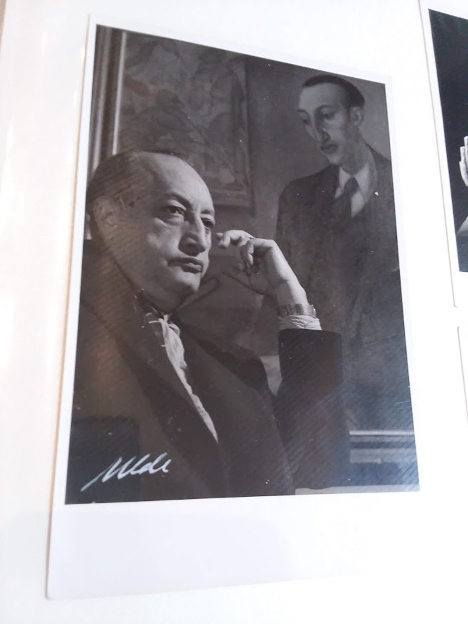

The Benson is the third repository to house materials pertaining to Asturias’s life work, the other two being the Bibliothèque nationale in Paris and El Archivo General de Centroamérica in Guatemala City. What differentiates this particular collection is the role that Asturias’s son, Miguel Ángel Asturias Amado, played in compiling it over the course of fifty years. Indeed, in many ways the collection is just as much the son’s as it is the father’s. It features years of correspondence between the two, who were separated after the elder was forced to leave Argentina in 1962. This was not the writer’s first time in exile: his stay in Argentina was due to the Guatemalan government, led by Carlos Castillo Armas, stripping his citizenship in 1954. The letters provide insight into Asturias as a father, writer, and eventual diplomat when democratically elected Guatemalan President Julio César Méndez Montenegro restored his citizenship and made him Ambassador to France in 1966. Moreover, scholars will find within these letters a number of short stories for children that would eventually be collected in the book El alhajadito (1962).
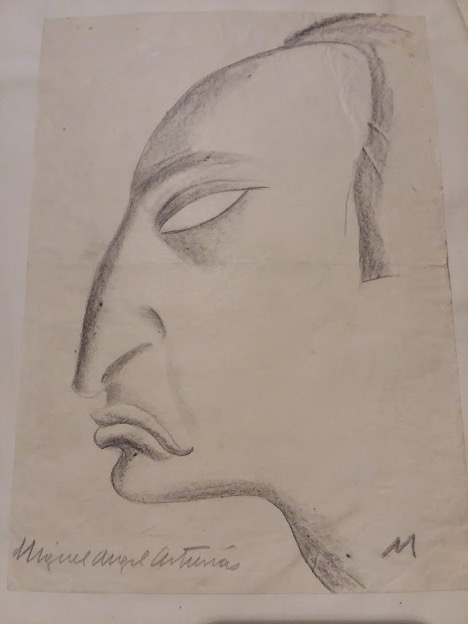

In addition to correspondence with his son, Asturias maintained a longstanding relationship with his mother via letter during his first stay in Paris in the 1920s. Detailed within are the family’s economic hardships as a result of the country-wide crisis in Guatemala caused by the plummeting international coffee market, and information pertaining to the publication of his first collection of short stories, Leyendas de Guatemala (1930). Other communication from this era demonstrates the role that Asturias played in facilitating the publication of other Guatemalan authors and as a journalist for El imparcial.

Beyond letters, scholars will find a multifaceted collection. Manuscripts of poetic prose, such as “Tras un ideal” (1917), and an early theater piece titled “Madre” (1918) are included with loose-leaf fragments from El señor presidente. News clippings are also prominent. Those written by Asturias reflect his time at El imparcial while those written about him focus on his Nobel Prize. Perhaps an unexpected highlight is the audiovisual component of the collection. The author contributed an array of caricatures, doodles, and portraits, as well as a robust collection of photographs. Furthermore, there are several audio recordings of Asturias reading his work.

Finally, scholars will also be able to access studies dedicated to the work of Asturias and first, rare, and special editions of his books. These editions, meticulously collected and cared for by his son, reflect the author’s continued popularity.
The addition of the Miguel Ángel Asturias Papers will bolster a growing collection of prominent Central American subject matter at the Benson that includes the Ernesto Cardenal Papers, the Pablo Antonio Cuadra Papers, the Victoria Urbano Papers, the Arturo Taracena Flores Collection, and the Digital Archive of the Guatemalan National Police Historical Archive. Once Benson staff can safely return to our offices, we will announce plans to process the collection . In the meantime, questions can be directed to Daniel Arbino, Benson Head of Collection Development, at d.arbino@austin.utexas.edu.
La Colección Benson adquiere el archivo del Premio Nobel Miguel Ángel Asturias
Por DANIEL ARBINO
La Colección Latinoamericana Nettie Lee Benson se complace en anunciar la adquisición de los documentos de Miguel Ángel Asturias, Premio Nobel de 1967. El autor guatemalteco fue un precursor del boom latinoamericano. Escritor prolífico de poesía, cuentos, literatura infantil, obras de teatro y ensayos, es quizás mejor conocido como novelista, y El señor presidente (1946) y Hombres de maíz (1949) son las más aclamadas. La representación de Guatemala y sus variados pueblos, creencias, interacciones, frustraciones y esperanzas, marcan la profundidad de sus textos.
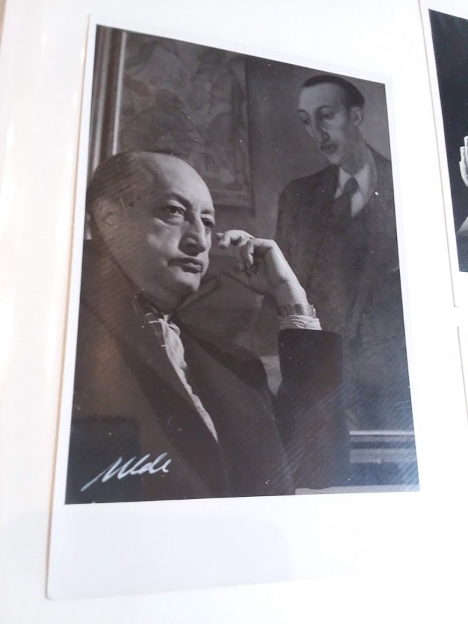

La Benson es el tercer archivo que reune materiales de la vida de Asturias, después de la Bibliothèque nationale en París y El Archivo General de Centroamérica en la ciudad de Guatemala. Lo que distingue a esta colección en particular es el papel que desempeñó el hijo de Asturias, Miguel Ángel Asturias Amado, en su recopilación a lo largo de cincuenta años. De hecho, la colección es, en muchos sentidos, tanto del hijo como del padre. Presenta años de correspondencia entre los dos, que se separaron después de que el padre tuvo que abandonar la Argentina en 1962. Ésta no fue la primera vez que el escritor se había tenido que ir al exilio: su estadía en la Argentina se debió a que el gobierno guatemalteco, liderado por Carlos Castillo Armas, le había despojado de su ciudadanía en 1954. Las cartas dan una idea de Asturias como padre, escritor y eventual diplomático, después de que Julio César Méndez Montenegro, el presidente de Guatemala democráticamente elegido, restauró su ciudadanía y lo nombró embajador en Francia en 1966. Además, los investigadores encontrarán dentro de estas cartas una serie de cuentos para niños que se recopilarían en el libro El alhajadito (1962).
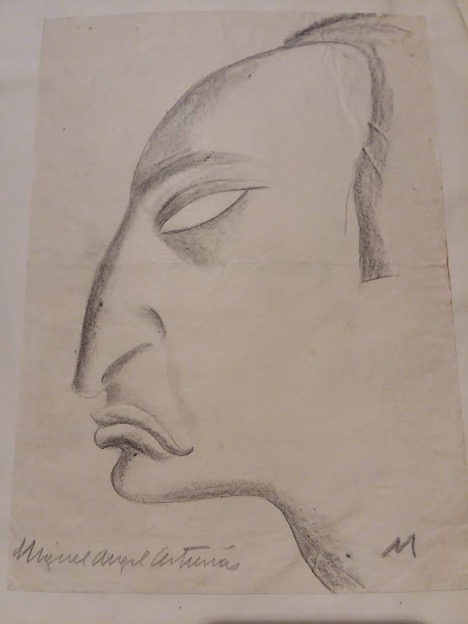

Aparte de la correspondencia con su hijo, Asturias mantuvo una larga relación epistolar con su madre durante su primera estancia en París en la década de los 1920. Ahí se detallan las dificultades económicas de la familia como resultado de la crisis que atraviesa la sociedad guatemalteca, por la caída del precio del café a nivel internacional, e información relativa a la publicación de su primera colección de cuentos, Leyendas de Guatemala (1930). Otra comunicación de esta época demuestra el papel que desempeñó Asturias al facilitar la publicación de otros autores guatemaltecos y como periodista de El imparcial.

Asimismo, los investigadores verán una colección multifacética. Los manuscritos de prosa poética, como “Tras un ideal” (1917) y una obra de teatro titulada “Madre” (1918) se incluyen, tanto como fragmentos de hojas sueltas de El señor presidente. Los recortes de periódicos también son prominentes. Los escritos por Asturias reflejan su tiempo en El imparcial, mientras que los escritos sobre él se centran en su Premio Nobel. Quizás un punto destacado inesperado es el componente audiovisual de la colección. El autor contribuyó con una serie de caricaturas, garabatos y retratos, así como una colección robusta de fotografías. También, hay varias grabaciones de audio de Asturias en las cuales realiza lecturas de sus obras.

Por último, los académicos también podrán acceder a los estudios dedicados al trabajo de Asturias y a las primeras, raras y especiales ediciones de su trabajo. Estas ediciones, meticulosamente recopiladas y cuidadas por su hijo, reflejan la continua popularidad del autor.
La adquisición de los documentos de Miguel Ángel Asturias reforzará una creciente colección de materiales destacados de Centroamérica en LLILAS Benson, que incluye el archivo de Ernesto Cardenal, el archivo de Pablo Antonio Cuadra, el archivo de Victoria Urbano, la colección de Arturo Taracena Flores y la colección digital del Archivo Histórico de la Policía Nacional (AHPN) de Guatemala. Una vez que el personal de Benson pueda regresar de manera segura a nuestras oficinas, pronto seguirán los planes para procesar la colección. Mientras tanto, las preguntas pueden dirigirse a Daniel Arbino, Jefe de Desarrollo de Colecciones de la Benson.