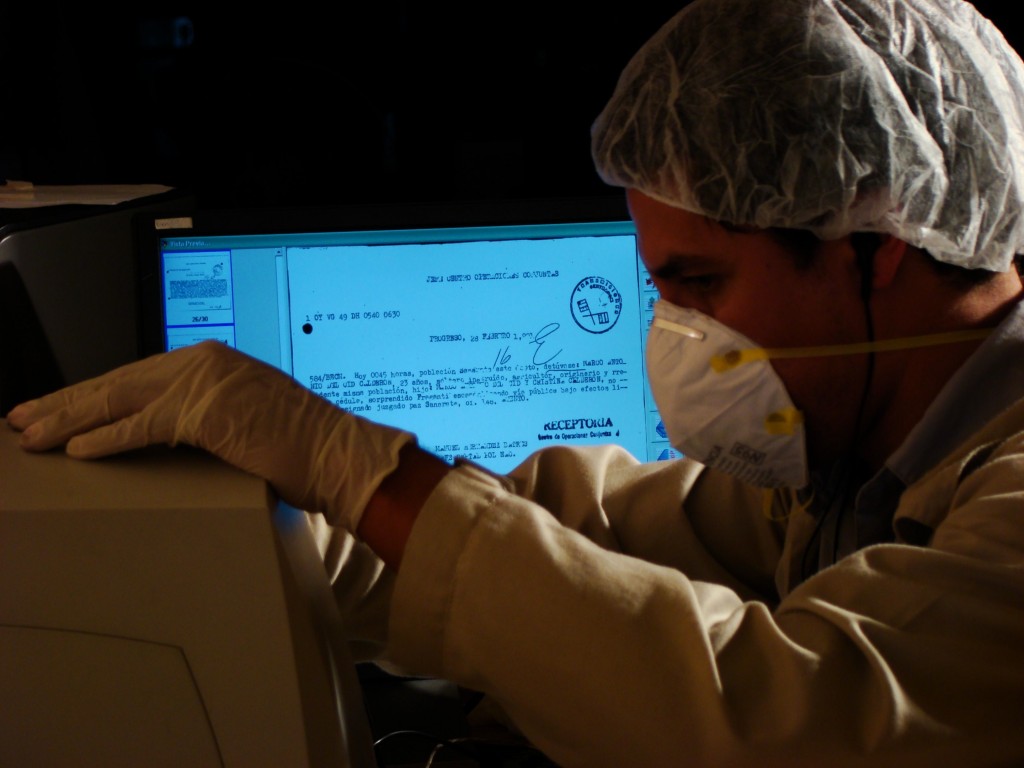
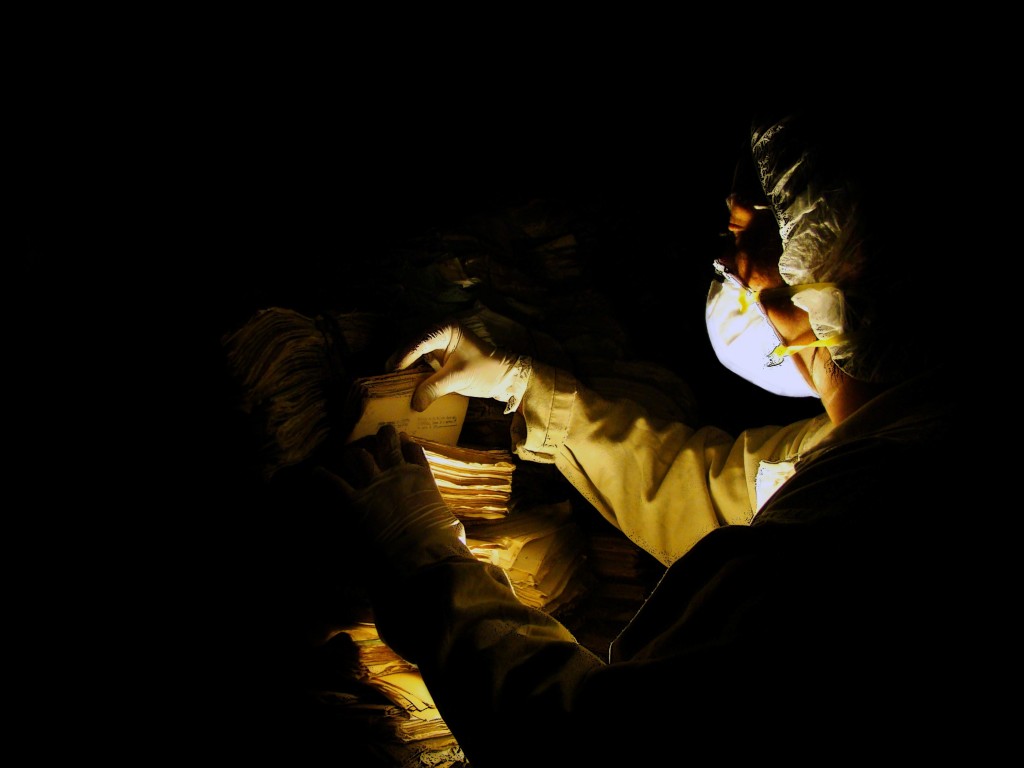
In recent weeks, actions taken by the government of Guatemala have put in jeopardy the future of the Historical Archive of the National Police of Guatemala (AHPN), a human rights archive with which LLILAS Benson and other units at the University of Texas at Austin have partnered since 2011.
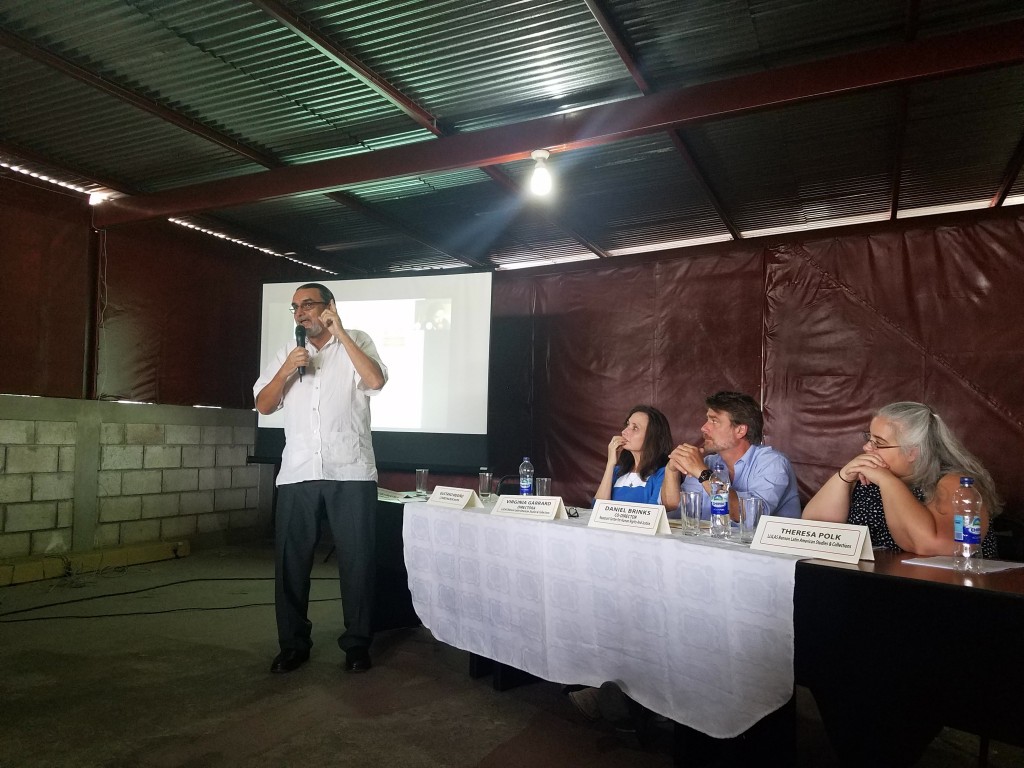
In a keynote speech to the Seminar on the Acquisition of Latin American Library Materials (SALALM), delivered on June 27 at the University of Texas at Austin, Guatemalan human rights activist Gustavo Meoño, former director of the AHPN, revealed some of the most recent events undermining the archive, including a drastic reduction of staff and an imminent takeover by the country’s Ministry of Culture, both of which have serious implications for the AHPN’s operation and integrity.

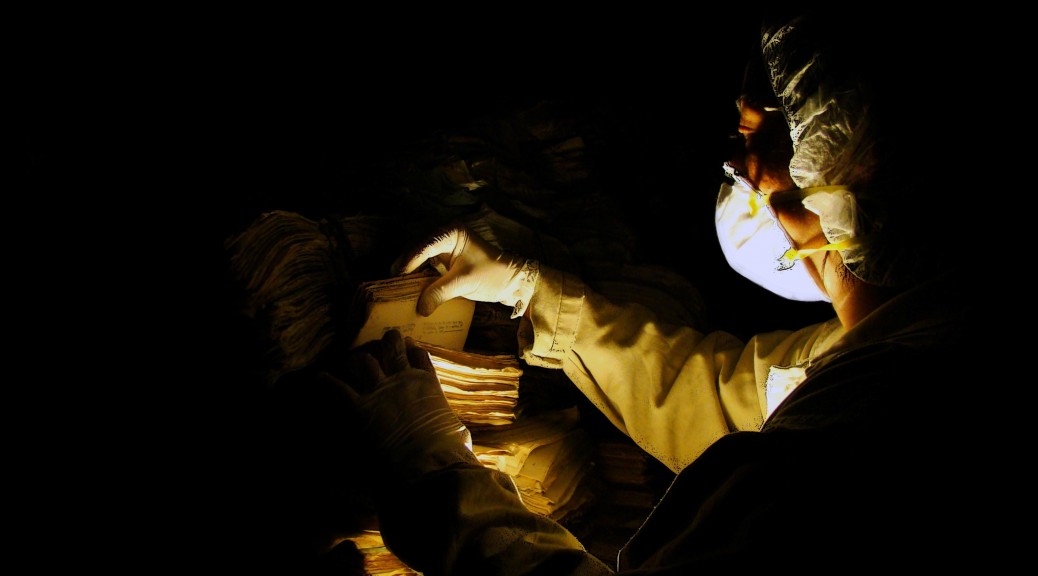
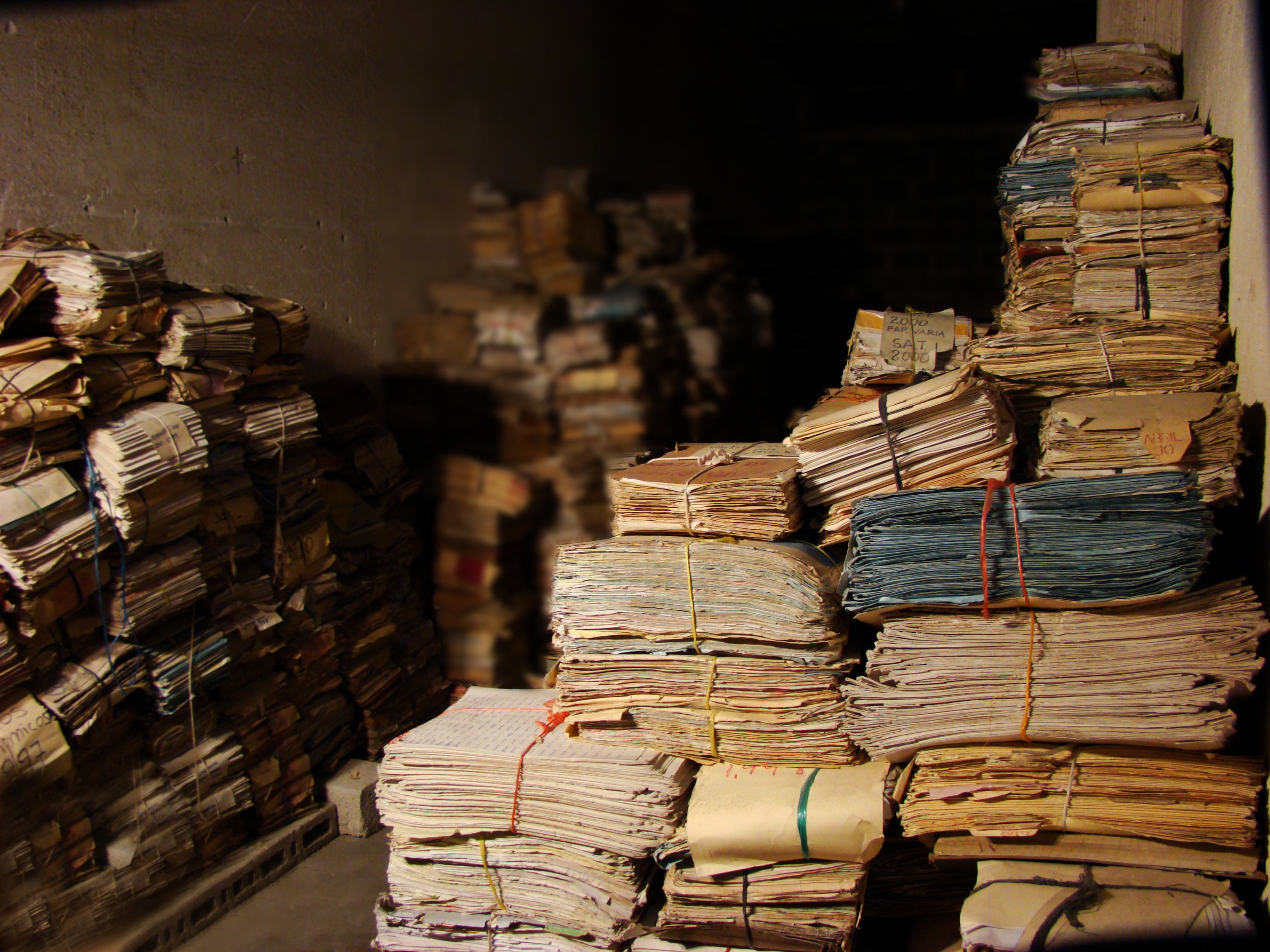
The significance of this news cannot be overstated. The AHPN contains records of Guatemala’s former National Police dating back more than a century. Its contents relating to the country’s 36-year armed conflict have been crucial in uncovering the fate of tens of thousands of Guatemalans during the most violent years of civil strife. “Since its discovery in 2005, the AHPN has played a central role in Guatemala’s attempts to reckon with its bloody past,” according to the National Security Archive, an NGO in Washington DC that advocates against government secrecy. The records “have been relied upon by families of the disappeared, scholars, and prosecutors. The institution has become a model across Latin America and around the world for the rescue and preservation of vital historical records,” an article dated May 30, 2019, states.
AHPN has become a model for the rescue and preservation of vital historical and human rights records.
Meoño served as director of the AHPN from 2005 until his abrupt removal in August 2018 at the hands of the Guatemalan government and the United Nations Development Office; he subsequently fled with his family to Argentina amid death threats and intimidation. In the weeks since his announcement in Austin, the fate of the AHPN has become even more uncertain. On July 10, the Ministry of Culture and Sports, which now oversees the archive, dismissed Anna Carla Ericastilla, longtime director of Guatemala’s national archive, the Archivo General de Centro América (AGCA, AHPN’s parent archive), amid accusations that she had illegally allowed access to the archive to entities outside the country, such as the University of Texas at Austin, and that she had collected donor contributions to pay archive personnel unbeknown to the Ministry of Culture and Sports.
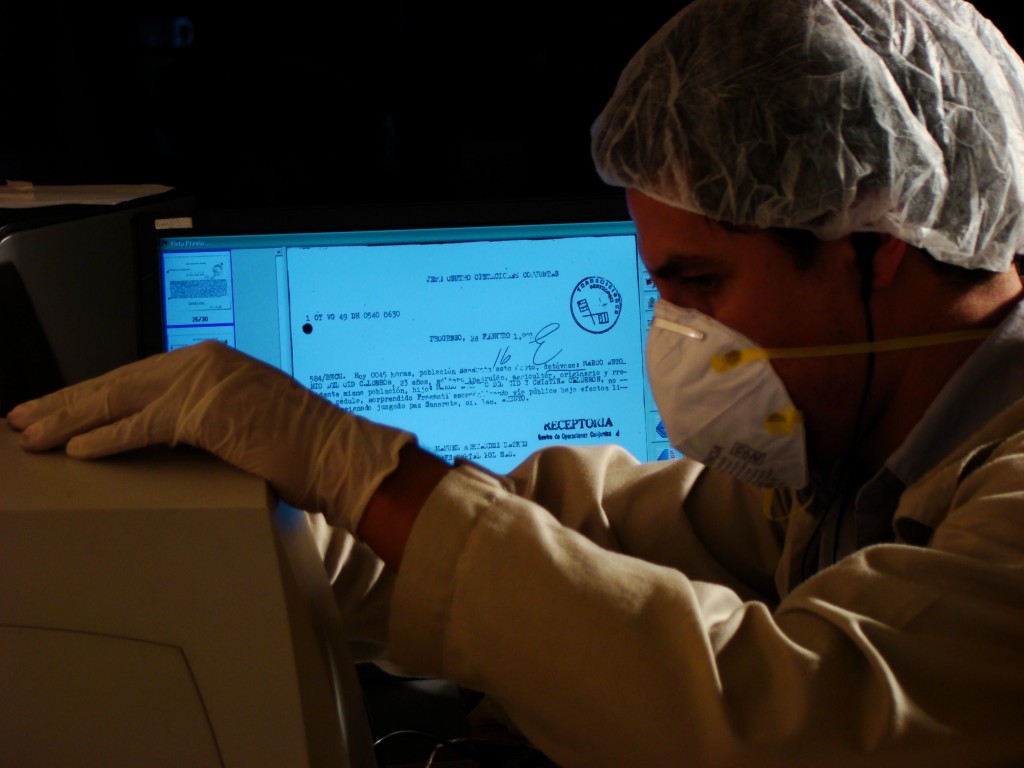

According to the AHPN website hosted by the University of Texas Libraries, “The AHPN Digital Archive is a collaborative project of the University of Texas’ Lozano Long Institute for Latin American Studies, Rapoport Center for Human Rights and Justice, and Benson Latin American Collection, with the Archivo Histórico de la Policía Nacional de Guatemala.” As faculty directors of the aforementioned institutions made clear in a recent letter to Guatemala’s minister and vice-minister of Culture and Sports, the collaboration with the AHPN and its parent archive, the AGCA, “has always been open, public, and fully in compliance with the laws of Guatemala and the United States.”

Documents from the AHPN have been used in 14 trials prosecuting human rights abuses, said Meoño. These include the 1980 burning by police of the Spanish Embassy in Guatemala City with 37 Indigenous protestors shut inside; and the 1981 abduction, rape, and torture of Emma Molina Theissen along with the subsequent forced disappearance of her 14-year-old brother Marco Antonio. Preservation efforts have prioritized documents from the worst years of government-sponsored terror, 1975–1985, according to Meoño. All told, there were almost 200,000 victims of the armed conflict, including the disappeared. “Indeed, it may be the Police Archive’s crucial contributions to human rights trials that caused the government of President Jimmy Morales to seek to control the repository and fire its director,” wrote the NSA last August.
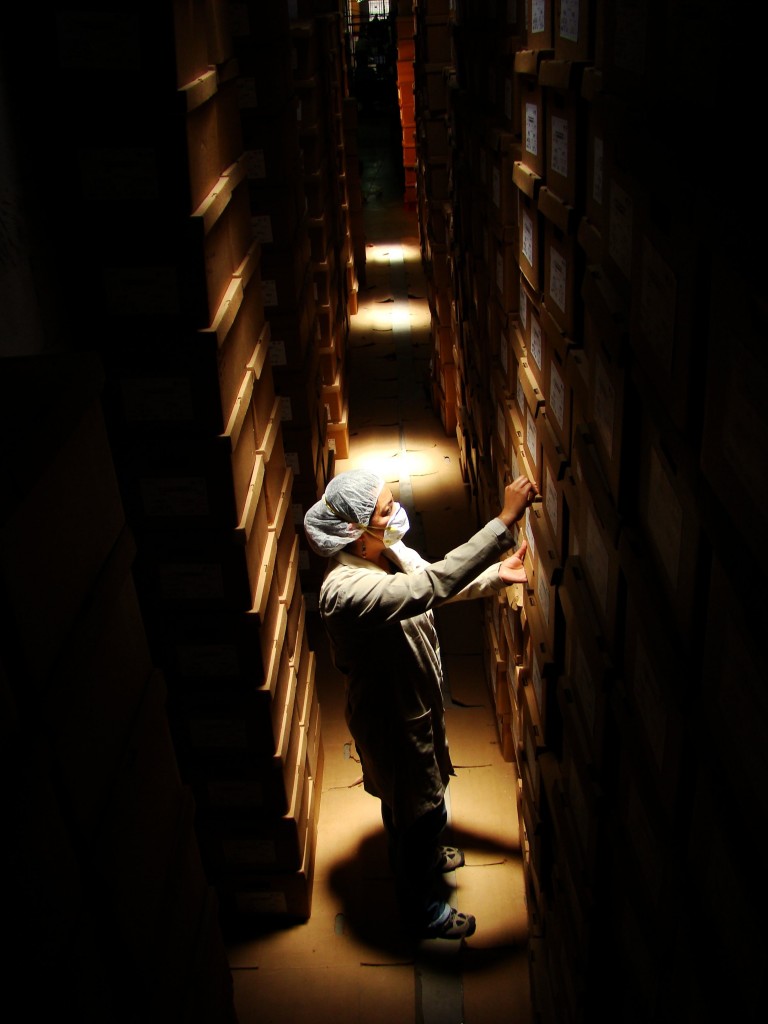

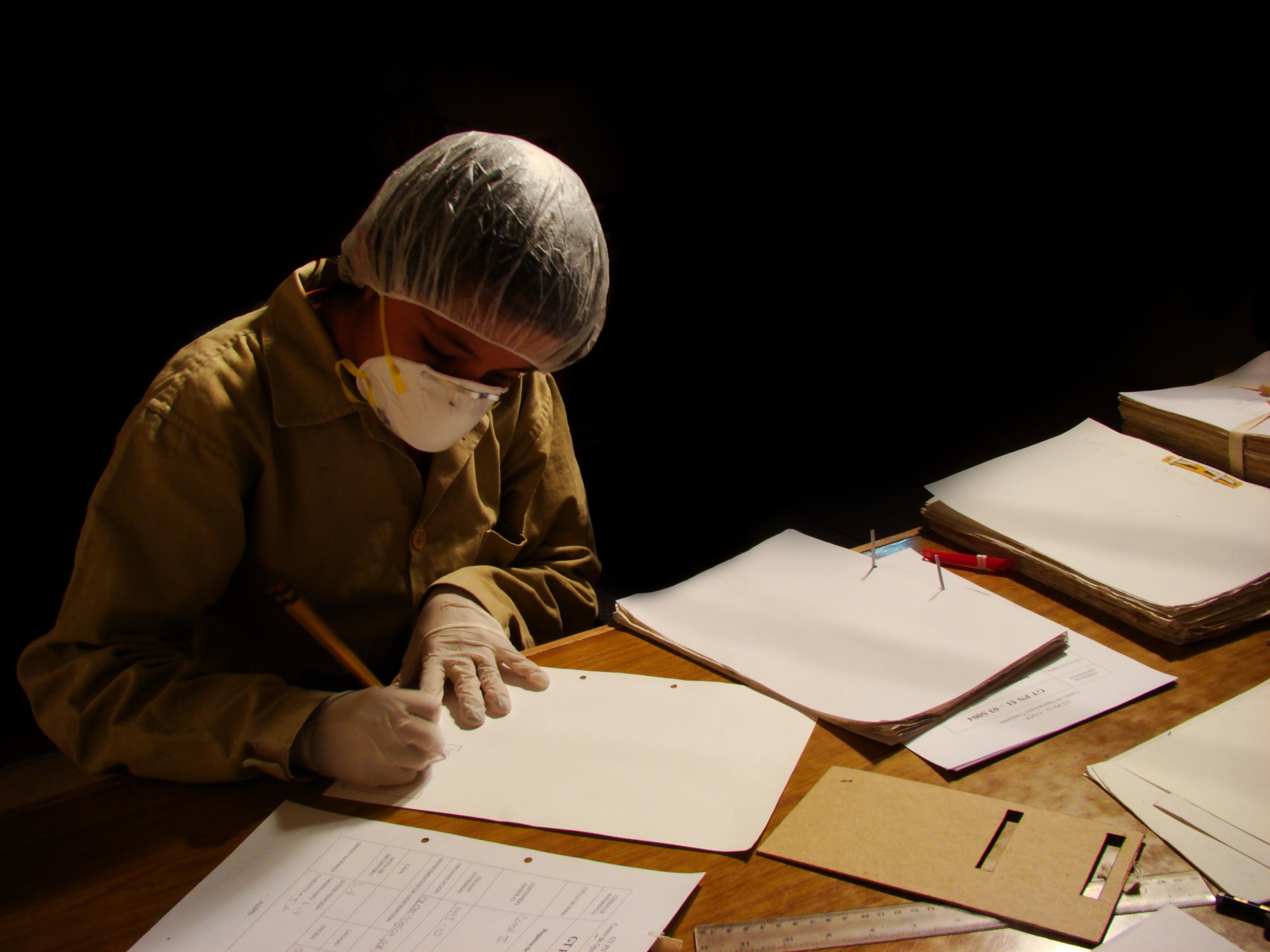
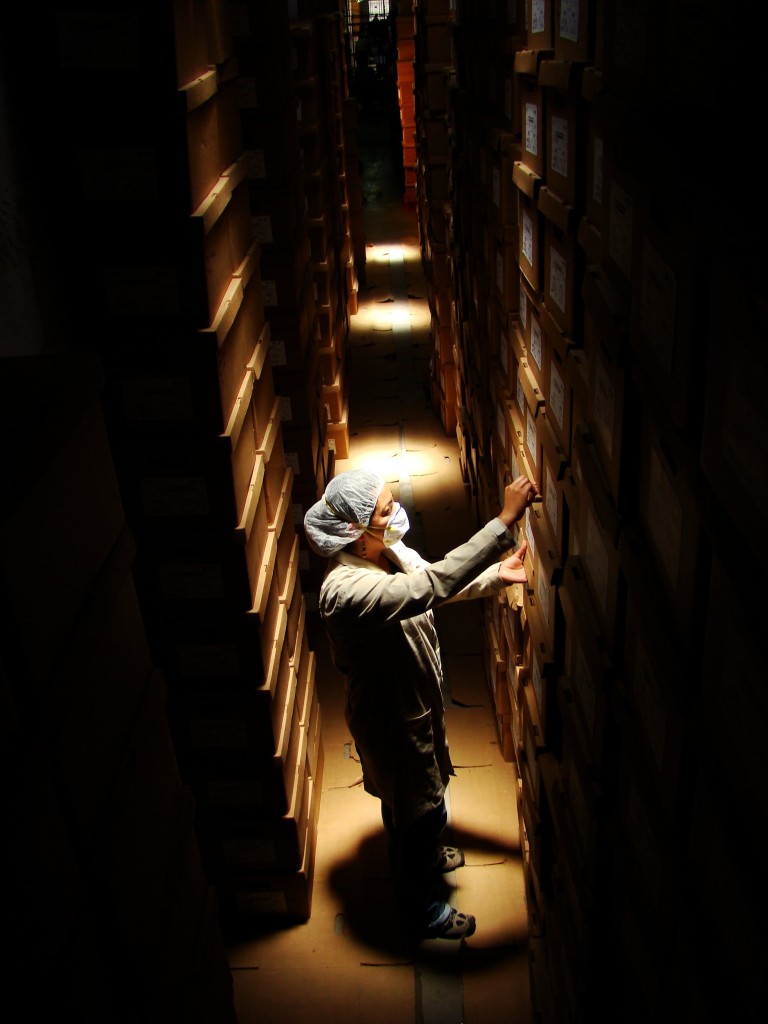
The fate of the AHPN has particular resonance for The University of Texas at Austin, and in particular, for LLILAS Benson Latin American Studies and Collections and the UT Libraries, who, through their partnership with the AHPN, have successfully secured and posted online digital copies of one-third of the more than 60 million documents in the archive—an estimated 8 linear kilometers of material. Preservation of the archive’s contents has been paramount since the documents were discovered, haphazardly stored, by the Guatemalan Office of the Human Rights Prosecutor (Procuraduría de los Derechos Humanos, or PDH) in filthy, rat-infested buildings that were part of a sprawling police base located in a Guatemala City neighborhood.
Guatemala will elect a new government in August. The AHPN’s Texas partners will be among the international community of human rights advocates watching closely to see what that bodes for the AHPN and the future of truth and restorative justice in Guatemala.
See related posts: 21 Years of Peace;, 21 Million Documents; 21 años de paz, 21 millones de documentos; Seminar Commemorates Collaboration with Guatemala on Archives and Human Rights