Read, hot & digitized: Librarians and the digital scholarship they love — In this new series, librarians from the UT Libraries Arts, Humanities and Global Studies Engagement Team briefly present, explore and critique existing examples of digital scholarship. Our hope is that these monthly reviews will inspire critical reflection of, and future creative contributions to, the growing fields of digital scholarship.
Government documents can offer crucial insight into the histories of a nation, but traditional access can require skill with microfilm readers, resources to travel to an archive and astute understanding of how to use an index. As cultural heritage institutions take on more digitization projects, researchers have benefited from remote access to digital collections complimented by user-friendly browse and search features. This past November, the National Museum of African American History and Culture (NMAAHC) gifted scholars and genealogists alike with the Freedmen’s Bureau Search Portal, a valuable new platform to discover 1.7 million pages of digitized records from the Bureau of Refugees, Freedmen, and Abandoned Lands.

Created in 1865, the Bureau of Refugees, Freedmen, and Abandoned Lands, more commonly known as the Freedmen’s Bureau, aspired to help Southerners, including 4 million formerly enslaved people, transition to a new society after the Civil War. Congress charged the Bureau with providing social support like medical care, rations and educational opportunities, and tried to help poor individuals deal with seized lands and find employment. Abolished in 1872 by Congress, the short-lived Bureau’s positive impact on assisting formerly enslaved people is still debated. However, the utility of these records for genealogical and scholarly purposes is certain as they offer valuable insight into the Reconstruction period, including government policies and interactions between freedmen, white southerners and government officials.
Previously, portions of these records have been available online for browsing, but were not always searchable or in one place. The NMAAHC interface allows users to filter records by collection, record type, location and date. In addition to a keyword search, these features help users discover materials like ledgers of employment, marriage records and reports describing criminal and civil disputes. Thanks to efforts to index names and locations, users can also search the names of enslaved and former owners, which is of particular use to genealogists and individuals researching family histories.
The indexing was the first step to the collection portal’s debut on the Smithsonian-developed digital asset management system, “Enterprise Digital Asset Network (EDAN)”. This system connects multiple Smithsonian digital collections and allows users to access metadata using the institution’s own API. The user-friendly search interface is built using the open source search platform, Apache Solr, which UT Libraries also uses for our own Collections portal.
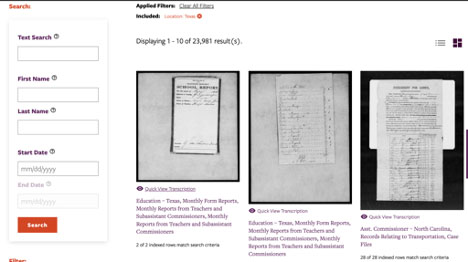
What makes the NMAAHC’s search portal especially notable is its support from a crowdsourcing transcription project, a collaborative endeavor from the NMAAHC and Smithsonian Transcription Center. This is the largest crowdsourcing project the Smithsonian has ever undertaken and so far, 400,000 pages have been transcribed by volunteers. The records’ cursive script makes it challenging to automatically transcribe using OCR, and the project will greatly benefit from transcription efforts. These efforts are invaluable as the letters and reports that provide more details beyond statistical ledgers are more often than not untranscribed.
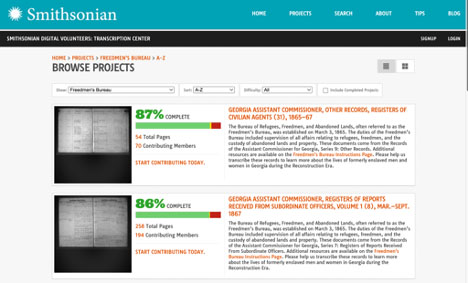
For now, users can still search the indexed data for names, places and dates, and additional information provided by volunteers in their transcription efforts like subjects and keywords. The records themselves and the transcription project will provide scholars a glimpse into life during the Reconstruction period and allow genealogy researchers to make meaningful connections with ancestors and family histories.
Explore more in these UT Libraries resources:
New UT Libraries Database! African American Heritage
- Digital resource exclusively devoted to an American family history research containing primary sources devoted specifically to African American family history, including census records, vital records, freedman and slave records, church records, legal records, and more.
Crouch, Barry A. The Freedmen’s Bureau and Black Texans. University of Texas Press, 1999.
Farmer-Kaiser, Mary. Freedwomen and the Freedmen’s Bureau: Race, Gender, and Public Policy in the Age of Emancipation. Fordham University Press, 2010.
Mears, Michelle M. And Grace Will Lead Me Home: African American Freedmen Communities of Austin, Texas, 1865-1928. Texas Tech University Press, 2009.

