Read, hot & digitized: Librarians and the digital scholarship they love — In this series, librarians from UTL’s Arts, Humanities and Global Studies Engagement Team briefly present, explore and critique existing examples of digital scholarship. Our hope is that these monthly reviews will inspire critical reflection of and future creative contributions to the growing fields of digital scholarship.
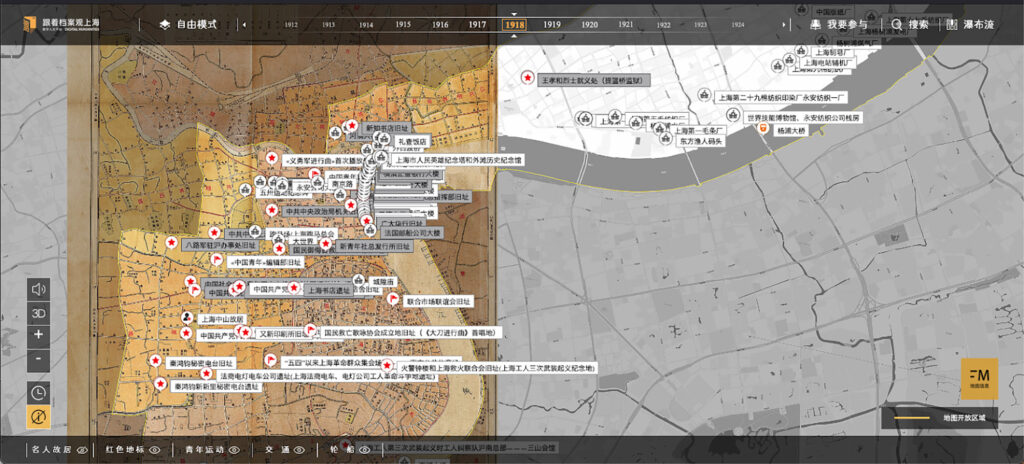
Among the candidates for the Best Data Visualization category in the 2023 Digital Humanities Award, I found this recent project from the Shanghai Archives (Shanghai dang an guan 上海檔案館, Following the Archives to Know Shanghai). The project beautifully takes viewers on a tour through Shanghai’s most significant historical sites. It is built on archival materials about over 100 city landmarks in Shanghai. All the sites are plotted onto georeferenced historical maps. Viewers can choose from 13 base historical maps ranging from 1855 to 2024 (The following screenshot features a base map from 1923). Currently, the site only supports Chinese as the interface language, but Google Translate does a sufficient job of making it navigable in English.
Shanghai, one of the first treaty ports that China opened to the West in the 1840s, grew into one of Asia’s biggest international metropolises and financial centers by the late nineteenth century. The city was home to many of modern China’s political, economic, and cultural elites, and its foreign concessions hosted thousands of foreign merchants, colonial officials, missionaries, and adventurers. Since the nineteenth century, the city also saw many major historical events that shaped modern China. For example, as the hub of China’s emerging modern/Westernized educational institutions, Shanghai was one of the centers of the May Fourth movement in 1919 that popularized Western political and scientific values to new generations of Chinese youth. Soon after, the Chinese Communist Party convened its national congress in the city in 1921. The city was also home to many international banks and manufacturing enterprises, which incubated the labor movements of the 1920s and 1930s. Beyond all these, the battles between the Chinese soldiers and invading Japanese forces in 1931 and 1937 were fought on the city’s streets while spies serving various regimes hustled throughout the city ruled by both Chinese and foreign authorities.
This project by the Shanghai Archives aims to present this complex and exciting history to the users. Sites are categorized into five categories: famous people’s residences (mingren guju 名人故居), revolutionary landmarks (hongse dibiao 红色地标), youth movements sites (qingnian yundong 青年运动), transportation infrastructures (jiaotong 交通), and ships and shipyards (lun chuan 轮船).
To explore a location, you click on it on the map, and a new window opens up on the right side, showing a timeline with documents related to the landmark. The following example shows eleven items related to the HSBC Bank building on the bund (waitan 外灘). Most items are historical photographs of the building, but the collection also contains a digitized copy of the bank’s stock certificate from 1894. The site also provides 3D models of the buildings for users to explore.
The project also provides audiovisual materials for some storied sites. For example, among the items related to the racecourse (Pao Ma Chang 跑馬場), there is a short documentary showing historical clips of events held there.
The project is commendable in making archival materials available to the public in an interactive and engaging way, although it does have a pronounced emphasis on the communists’ activities in presenting the story map. As metadata is the foundation of all digital humanities projects, I am compelled to comment that the metadata of presented archival items leaves much to be desired. In the map view, items are only provided with title, source, and year, without any identifying numbers linking back to the Archives or its partner institutions. The browse view features a waterfall layout like Pinterest, which may be compelling to some but unfortunately does not provide more metadata than the story map view.
Overall, the site offers an engaging journey through Shanghai’s recent past. It is exciting to see more locations and archival materials being added. I hope the quality of metadata can be enhanced one day. It would also be great if the textual documents could be OCRed and searched in full text.
Learn more about Shanghai and its history:
Dian Shi Zhai hua bao: A Major Shanghai-based pictorial magazine (1884–1898).
Liang You: Shanghai-based popular magazine published from 1926 to 1945.
Leo Ou-fan Lee, Shanghai Modern: the Flowering of a New Urban Culture in China, 1930–1945 (Harvard University Press, 1999).
Jin Jiang, Women Playing Men: Yue Opera and Social Change in Twentieth-Century Shanghai (Seattle: University of Washington Press, 2009)
Frederick Wakeman, Policing Shanghai 1927-1937 (Berkeley: University of California Press, 1995).