If you’ve spent much time in the past decade or so traveling in Texas, you might have noticed the increasing ubiquity of wind farms cropping up along spartan stretches of highway across the state. If a new project involving a fellowship recipient in residence at the Libraries holds any promise, you might soon see more solar panels along your travels, as well.

Last August, the university welcomed a new Council on Library and Information Resources (CLIR) fellow, Emily Beagle, who spent the fall splitting time between the Research Support & Digital Initiatives at the Libraries and the Webber Energy Group in the Mechanical Engineering Department. Beagle was one of a group of four cohorts in a Data Curation for Energy Economics track for CLIR who are working at various energy institutes and libraries across the country. Beagle’s specific project work throughout the fall related to a renewable energy project funded through The Ray (at The Ray C. Anderson Foundation in Georgia) — one that could potentially bring solar power generation to those long stretches of Texas highway.
The Ray began as a project specific to an 18-mile stretch of I-85 southwest of Atlanta as an exploration of ways “to create a regenerative highway ecosystem” through a reconsideration of the land and communities surrounding our collective highway system. The Ray has already deployed several pilot technology projects along the route including solar-powered vehicle charging, a tire safety check station and solar-paved highways, and the component of the project tasked to the Webber Group was to investigate the placement of solar photovoltaic panels along the right-of-ways nationwide to provide additional energy to the power grid. To do so, the group had to consider the over 45,000 miles of roadways that make up the U.S. interstate network.
Narrowing the scope down to a manageable sampling required the research group to come up with some exclusionary criteria, removing swaths from consideration like protected areas (e.g. National Parks and Forests), and focusing on locations close to existing transmission lines, adjacent spaces that are large enough to accommodate development, and locations near exits to make them easy for maintenance access. This allowed them to use existing environmental data for the available space to determine where voltaic clusters would be most efficient and effective.
The Webber Group’s work on The Ray project began in March before Beagle arrived, but that worked out well for her contribution to the project, which involved the development of a data management plan, prepping data for sharing and preservation in repositories like Texas ScholarWorks, and validating reproducibility in findings. She has worked closely with Libraries colleagues to develop and implement the data plans for the group, while also providing ongoing assessment of the process and the effectiveness of Libraries’ tools and resources as an embedded member of the project team.
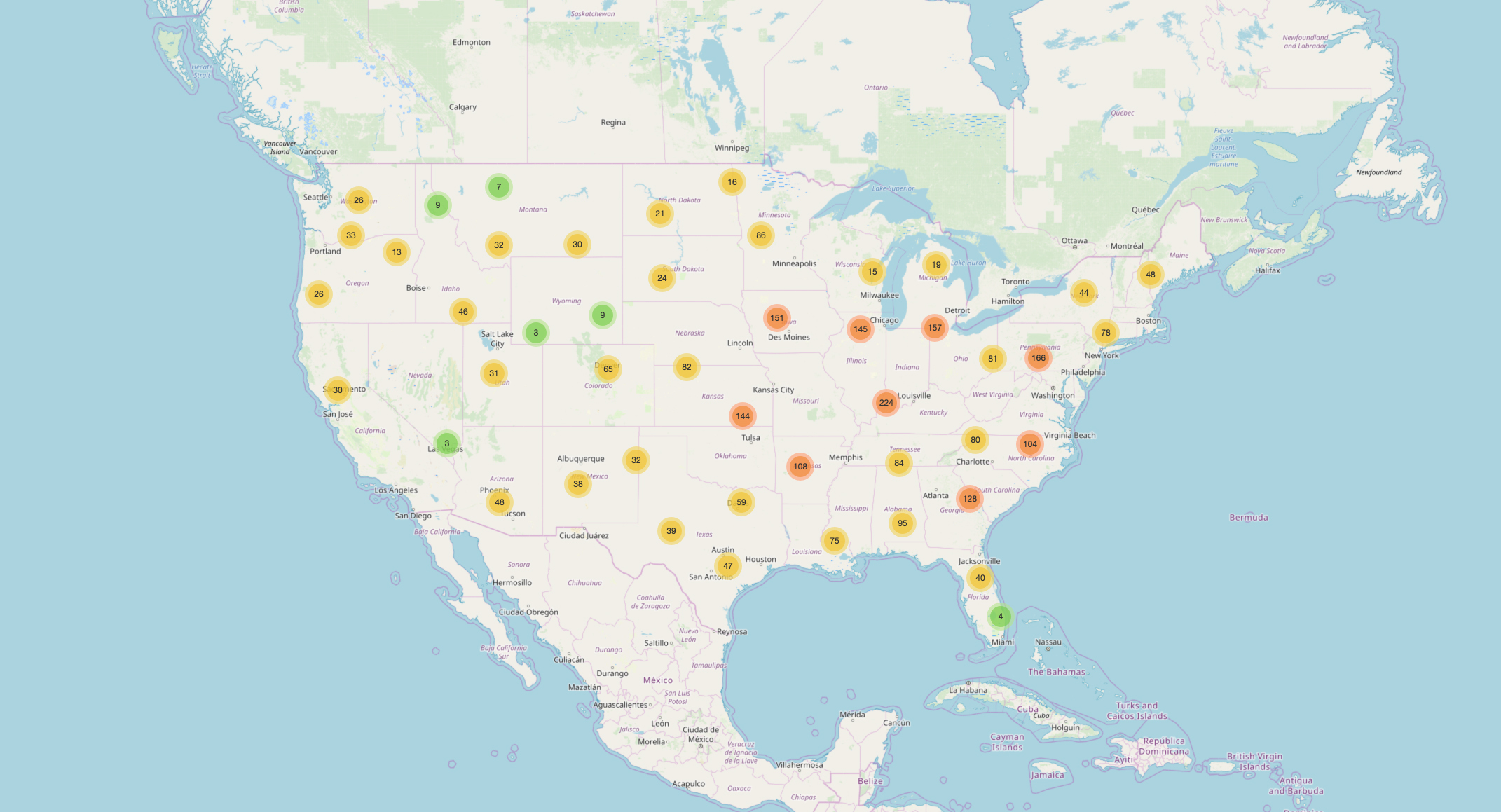
Working throughout the fall, the group was able to create a report for the foundation in December, and develop an online tool — the Solar Potential Map — that shows the best options for locating panel installations along roadways across the U.S. With the potential for a significant national infrastructure investment under discussion, components conceptualized through a project like The Ray could eventually become a reality. The Ray has already piloted one cluster of solar panels along I-85, and now they have the data to support an expansion of the idea on a much larger scale.
Beagle will continue her stint as a CLIR fellow through the spring, coordinating with her peers in Mechanical Engineering to supervise graduate student work on data-intensive research projects and use that interface to inform and develop data management resources and services at the Libraries. She’ll also using the knowledge she’s gained from the fellowship residence to co-teach workshops for other researchers on campus.
She isn’t the first CLIR fellow the Libraries have hosted — there are currently two Postdoctoral Fellows for Data Curation in Latin American and Latina/o Studies at the Benson Latin American Collection: Edward Shore (continuing from 2017) is overseeing a project to preserve and digitize rare historical documentation on quilombos, communities organized by fugitive slaves in colonial Brazil, and Jennifer Isasi (2018) is working with Benson Digital Scholarship Coordinator Albert A. Palacios to contribute to collections as data efforts, educational resources and digital scholarship initiatives at LLILAS Benson Latin American Studies and Collections. And 2017 fellow at the Benson, Hannah Alpert-Abrams, recently completed her term working to develop the repository and interface for the digital Archivo Histórico de la Policía Nacional, a collection of records relating to the national police of Guatemala. 2013 CLIR Postdoctoral Fellow for Data Curation in Medieval Studies Ece Turnator took part in a collaborative bid between the Libraries, the English Department and research units on campus — including the Texas Advanced Computing Center — to create a global gateway to all the digital resources currently available on the Middle Ages, the Global Middle Ages Project (G-MAP).
“The CLIR program has been of great value to the Libraries by allowing us access to trained scholars and researchers with perspectives informed by current trends in the interrelationship between libraries and community stakeholders,” says Vice Provost Lorraine Haricombe. “Their presence provides an opportunity to bridge between unit-level research and scholarship and library resources and services, and to use that bridge to improve and elevate what we do.”
The CLIR Postdoctoral Fellowship Program offers recent Ph.D. graduates the chance to help develop research tools, resources, and services while exploring new career opportunities. Host institutions benefit from fellows’ field-specific expertise by gaining insights into their collections’ potential uses and users, scholarly information behaviors and current teaching and learning practices within particular disciplines.
Beagle says the fellowship experience so far has played out as advertised, but in unexpected ways.
“Being split between Engineering and the Libraries, I was expecting that my duties for both would be very different and not have much overlap,” she says. “But I have been pleasantly surprised at how much I have been able to collaborate between the two groups and how much work in one area has informed a project in the other.”
“It has been very rewarding to work with the Webber Energy Group, UT Libraries and The Ray on a project with real world applicability. I hope to someday see solar panels along the interstate and be able to think ‘I was a part of that.’”




