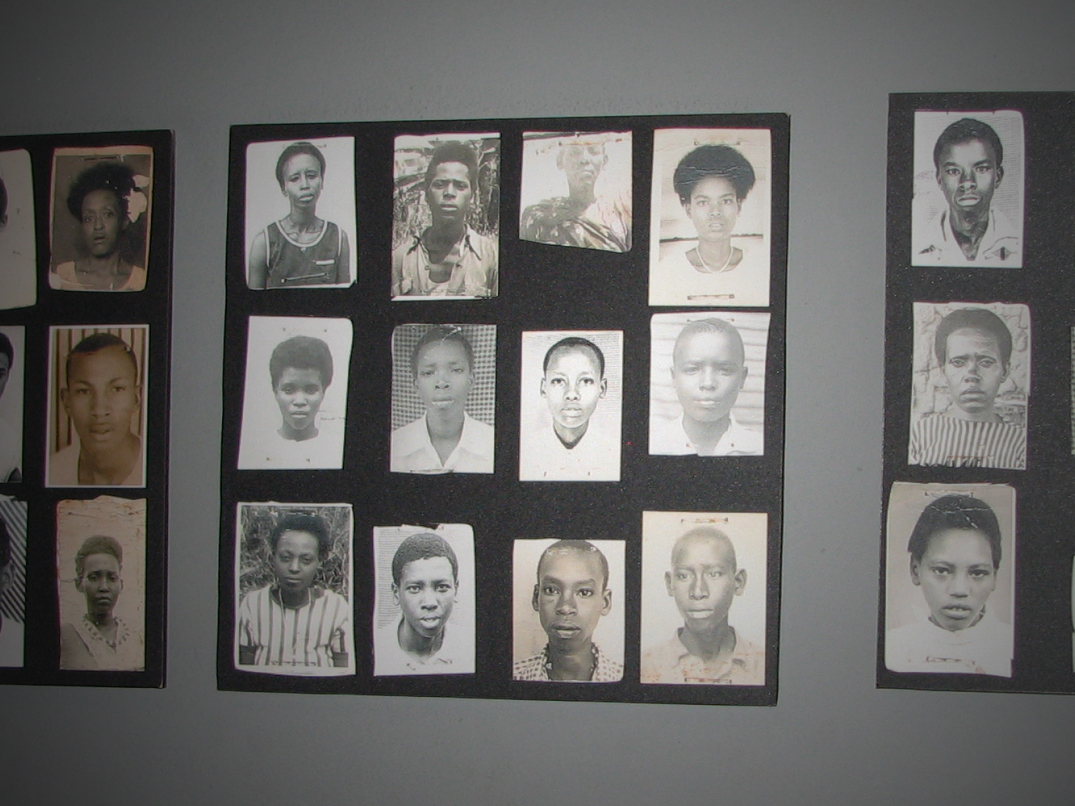
On June 9 — International Archives Day — the Libraries’ Human Rights Documentation Initiative (HRDI) partners Aegis Trust and the Kigali Genocide Memorial Centre launched a new, greatly updated and expanded online Genocide Archive of Rwanda (http://www.genocidearchiverwanda.org.rw).
One of the most important resources online documenting the causes, processes, and consequences of the 1994 Genocide against the Tutsi, GAR demonstrates the generative impact that the Libraries’ programming can have. The HRDI project, begun in Rwanda in 2008, engaged staff and volunteers at the Kigali Genocide Memorial Centre, a museum and documentation center for education and memory in Rwanda, to combine their personal experiences, deep knowledge, and historical resources with the technical expertise at UT Libraries in order to preserve and provide access to the fragile record of the Genocide that was daily being lost.
 The first version of GAR, developed by the Libraries’ Technology Integration Services, Information Technology Architecture and Strategy, and Digitization Services departments using Glifos media software, was installed on a laptop and hand-carried by me and human rights archivist T-Kay Sangwand to Rwanda, where it spent the next year demoing the project to build local community, government, and international support.
The first version of GAR, developed by the Libraries’ Technology Integration Services, Information Technology Architecture and Strategy, and Digitization Services departments using Glifos media software, was installed on a laptop and hand-carried by me and human rights archivist T-Kay Sangwand to Rwanda, where it spent the next year demoing the project to build local community, government, and international support.
Launched online in 2010, GAR enabled people in Rwanda and around the world to hear testimonies from Genocide survivors as well as perpetrators and elders in Rwanda about their experiences of Genocide, its root causes, and the lives and society that it destroyed. Photographs and historical documents were collected and digitized by Aegis Trust’s Rwandan staff to be added to the  Archive and preserved digitally by UT Libraries, and soon UTL was consulting on construction of a climate-controlled physical archive in Kigali in addition to the online digital archive.
Archive and preserved digitally by UT Libraries, and soon UTL was consulting on construction of a climate-controlled physical archive in Kigali in addition to the online digital archive.
The new Genocide Archive of Rwanda moves the archive to the cloud and integrates new mapping features, improved access to documents and photographs, and interactive tours of memorial sites around the country. The new site also includes features to engage youth in peace-building, and highlights important community renewal and reconciliation programs.
When recently retired Vice Provost Dr. Fred Heath and I attended the Kwibuka 20 commemoration ceremonies marking 20 years since the Genocide, Rwandan president Paul Kagame stated that, “Historical clarity is a duty of memory that we cannot escape. Behind the words ‘Never Again’, there is a story whose truth must be told in full, no matter how uncomfortable.” Born in the basement at Perry-Castañeda Library, and now managed in the cloud by a team of new information professionals in Rwanda, the Genocide Archive of Rwanda is a resource that preserves and gives clarity to the 1994 Genocide in support of memory, reconciliation, education, and scholarship in Rwanda, Texas, and around the globe.
The global impact of the University of Texas Libraries is made possible in large part to the financial support of individual, corporate and foundation donors. To contribute to projects like the Human Rights Digitization Project, please contact Natalie Moore or visit our online giving page today.